In vivo reprogramming of NG2 glia enables adult neurogenesis and functional recovery following spinal cord injury
- PMID: 33675690
- PMCID: PMC8106641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.02.009
In vivo reprogramming of NG2 glia enables adult neurogenesis and functional recovery following spinal cord injury
Abstract
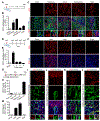
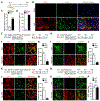
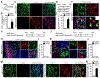
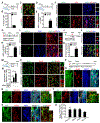
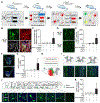
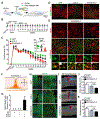
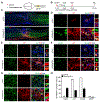
Adult neurogenesis plays critical roles in maintaining brain homeostasis and responding to neurogenic insults. However, the adult mammalian spinal cord lacks an intrinsic capacity for neurogenesis. Here we show that spinal cord injury (SCI) unveils a latent neurogenic potential of NG2+ glial cells, which can be exploited to produce new neurons and promote functional recovery after SCI. Although endogenous SOX2 is required for SCI-induced transient reprogramming, ectopic SOX2 expression is necessary and sufficient to unleash the full neurogenic potential of NG2 glia. Ectopic SOX2-induced neurogenesis proceeds through an expandable ASCL1+ progenitor stage and generates excitatory and inhibitory propriospinal neurons, which make synaptic connections with ascending and descending spinal pathways. Importantly, SOX2-mediated reprogramming of NG2 glia reduces glial scarring and promotes functional recovery after SCI. These results reveal a latent neurogenic potential of somatic glial cells, which can be leveraged for regenerative medicine.
Keywords: NG2 glia; SOX2; adult neurogenesis; astrocytes; ependymal cells; glial scar; in vivo reprogramming; lineage tracing; monosynaptic connections; spinal cord injury.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Barnabe-Heider F, Goritz C, Sabelstrom H, Takebayashi H, Pfrieger FW, Meletis K, and Frisen J (2010). Origin of new glial cells in intact and injured adult spinal cord. Cell stem cell 7, 470–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

