Understanding and treating the inflammatory adverse events of cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 33675691
- PMCID: PMC7979511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.011
Understanding and treating the inflammatory adverse events of cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
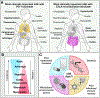
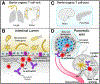
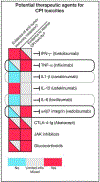
During the past decade, immunotherapies have made a major impact on the treatment of diverse types of cancer. Inflammatory toxicities are not only a major concern for Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved checkpoint blockade and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies, but also limit the development and use of combination therapies. Fundamentally, these adverse events highlight the intricate balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory pathways that regulate protective immune responses. Here, we discuss the cellular and molecular mechanisms of inflammatory adverse events, current approaches to treatment, as well as opportunities for the design of immunotherapies that limit such inflammatory toxicities while preserving anti-tumor efficacy.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests K.W.W. serves on the scientific advisory board of TCR2 Therapeutics, T-Scan Therapeutics, SQZ Biotech, and Nextechinvest and receives sponsored research funding from Novartis. He is a scientific co-founder of Immunitas Therapeutics. M.D. is a consultant for Tillotts Pharma, Partner Therapeutics, and Genentech-Roche, receives research funding from Novartis, and is on the Scientific Advisory Board for Neoleukin Therapeutics. S.K.D. receives research funding from Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Eli Lilly and is a scientific co-founder of Kojin.
Figures


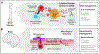
References
-
- Arbour KC, Mezquita L, Long N, Rizvi H, Auclin E, Ni A, Martinez-Bernal G, Ferrara R, Lai WV, Hendriks LEL, et al. (2018). Impact of Baseline Steroids on Efficacy of Programmed Cell Death-1 and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Blockade in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J Clin Oncol 36, 2872–2878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

