Characterization of axolotl lampbrush chromosomes by fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunostaining
- PMID: 33675804
- PMCID: PMC8123938
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112523
Characterization of axolotl lampbrush chromosomes by fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunostaining
Abstract
The lampbrush chromosomes (LBCs) in oocytes of the Mexican axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) were identified some time ago by their relative lengths and predicted centromeres, but they have never been associated completely with the mitotic karyotype, linkage maps or genome assembly. We identified 9 of the axolotl LBCs using RNAseq to identify actively transcribed genes and 13 BAC (bacterial artificial clone) probes containing pieces of active genes. Using read coverage analysis to find candidate centromere sequences, we developed a centromere probe that localizes to all 14 centromeres. Measurements of relative LBC arm lengths and polymerase III localization patterns enabled us to identify all LBCs. This study presents a relatively simple and reliable way to identify each axolotl LBC cytologically and to anchor chromosome-length sequences (from the axolotl genome assembly) to the physical LBCs by immunostaining and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Our data will facilitate a more detailed transcription analysis of individual LBC loops.
Keywords: Ambystoma mexicanum; Axolotl; BAC FISH; Centromere; Lampbrush chromosomes.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures

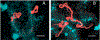

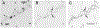

Similar articles
-
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization of DNA Probes on Mitotic Chromosomes of the Mexican Axolotl.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2562:165-173. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2659-7_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36272074
-
High-resolution mapping and transcriptional activity analysis of chicken centromere sequences on giant lampbrush chromosomes.Chromosome Res. 2012 Dec;20(8):995-1008. doi: 10.1007/s10577-012-9321-0. Chromosome Res. 2012. PMID: 23143648
-
Genetic mapping in the Mexican axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum.Can J Genet Cytol. 1984 Feb;26(1):1-6. doi: 10.1139/g84-001. Can J Genet Cytol. 1984. PMID: 6704787
-
Avian lampbrush chromosomes: a powerful tool for exploration of genome expression.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009;124(3-4):251-67. doi: 10.1159/000218130. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19556778 Review.
-
Structure of MHC class I and class II cDNAs and possible immunodeficiency linked to class II expression in the Mexican axolotl.Immunol Rev. 1998 Dec;166:259-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01268.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9914918 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the somatic TADs and lampbrush chromomere-loop complexes in transcriptionally active prophase I oocytes.Chromosoma. 2022 Dec;131(4):207-223. doi: 10.1007/s00412-022-00780-5. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Chromosoma. 2022. PMID: 36031655
References
-
- Flemming W, Zellsubstanz, Kern und Zelltheilung, F.C.W Vogel, Leipzig, 1882.
-
- Rückert J, Zur Entwicklungsgeschichte des Ovarialeies bei Selachiern, Anat. Anzeiger 7 (1892) 107–158.
-
- Gall J, Diaz M, Stephenson EC, Mahon KA, The transcription unit of lampbrush chromosomes, in: Subtelny S, Kafatos F(Eds.), Gene Struct Regul Dev vol. 41, 1983, pp. 137–146.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

