EQ-5D-5L reference values for the German general elderly population
- PMID: 33676523
- PMCID: PMC7937199
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-021-01719-7
EQ-5D-5L reference values for the German general elderly population
Abstract
Background: Reference values are a helpful tool to facilitate comparisons of sampled values against a specified reference population. The aim is to describe the health profile and to provide visual analogue scale (EQ VAS) and utility reference values for the EQ-5D-5L from a normative sample of the general elderly population (65+) in Germany.
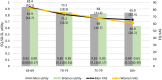
Methods: We analysed a sub-set of data from the German EQ-5D-5L valuation study using self-reported information based on EQ-5D-5L. We examined the share of respondents in each severity level per dimension as well as means, standard deviations (SD) and 95% confidence intervals for the index and EQ VAS values stratified by age groups and gender. Age was categorised in four groups (65-69, 70-74, 75-79 and > 79 years) to facilitate a more detailed examination of age-related health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
Results: The average index and EQ VAS scores were 0.84 (SD 0.22) and 73.2 (SD 18.5), respectively. In total, 21.4% reported no problems in all dimensions. With higher age, health problems were reported more frequently, which, in turn, lead to monotonically decreasing index and EQ VAS values. Overall, men reported fewer problems than women and this difference was largest beyond the age of 80.
Conclusion: HRQoL in the oldest old appears to be less stable and differs from the young elderly. However, the conventional age categorisation of earlier population norms studies seems to mask these differences. Hence, the more detailed provision of EQ-5D-5L reference values for the elderly population seems helpful for future German studies.
Keywords: EQ-5D-5L; Health state utilities; Health-related quality of life; Population norms; Reference values.
Conflict of interest statement
OM and WG are members of the EuroQol Group. There are no other competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Brazier J, Ratcliffe J, Salomon JA, Tsuchiya A. Measuring and valuing health benefits for economic evaluation. 2. New York: Oxford Univ. Pr; 2017.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources