Accurate determination of genotypic variance of cell wall characteristics of a Populus trichocarpa pedigree using high-throughput pyrolysis-molecular beam mass spectrometry
- PMID: 33676543
- PMCID: PMC7937246
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-021-01908-y
Accurate determination of genotypic variance of cell wall characteristics of a Populus trichocarpa pedigree using high-throughput pyrolysis-molecular beam mass spectrometry
Abstract
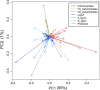
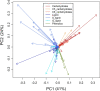
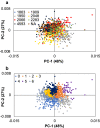
Background: Pyrolysis-molecular beam mass spectrometry (py-MBMS) analysis of a pedigree of Populus trichocarpa was performed to study the phenotypic plasticity and heritability of lignin content and lignin monomer composition. Instrumental and microspatial environmental variability were observed in the spectral features and corrected to reveal underlying genetic variance of biomass composition.
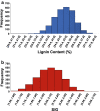
Results: Lignin-derived ions (including m/z 124, 154, 168, 194, 210 and others) were highly impacted by microspatial environmental variation which demonstrates phenotypic plasticity of lignin composition in Populus trichocarpa biomass. Broad-sense heritability of lignin composition after correcting for microspatial and instrumental variation was determined to be H2 = 0.56 based on py-MBMS ions known to derive from lignin. Heritability of lignin monomeric syringyl/guaiacyl ratio (S/G) was H2 = 0.81. Broad-sense heritability was also high (up to H2 = 0.79) for ions derived from other components of the biomass including phenolics (e.g., salicylates) and C5 sugars (e.g., xylose). Lignin and phenolic ion abundances were primarily driven by maternal effects, and paternal effects were either similar or stronger for the most heritable carbohydrate-derived ions.
Conclusions: We have shown that many biopolymer-derived ions from py-MBMS show substantial phenotypic plasticity in response to microenvironmental variation in plantations. Nevertheless, broad-sense heritability for biomass composition can be quite high after correcting for spatial environmental variation. This work outlines the importance in accounting for instrumental and microspatial environmental variation in biomass composition data for applications in heritability measurements and genomic selection for breeding poplar for renewable fuels and materials.
Keywords: Biomass composition; Heritability; Phenotypic plasticity; Poplar; Pyrolysis-molecular beam mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Abundance of Major Cell Wall Components in Natural Variants and Pedigrees of Populus trichocarpa.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 3;13:757810. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.757810. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35185975 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning-Based Classification of Lignocellulosic Biomass from Pyrolysis-Molecular Beam Mass Spectrometry Data.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4107. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084107. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921121 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid screening of secondary aromatic metabolites in Populus trichocarpa leaves.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023 Mar 10;16(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13068-023-02287-2. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023. PMID: 36899393 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput screening of plant cell-wall composition using pyrolysis molecular beam mass spectroscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;581:169-83. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-214-8_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19768623 Review.
-
NIR and Py-mbms coupled with multivariate data analysis as a high-throughput biomass characterization technique: a review.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Aug 7;5:388. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00388. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25147552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-resolution mapping reveals hotspots and sex-biased recombination in Populus trichocarpa.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Jan 12;13(1):jkac269. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac269. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 36250890 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecific variability in plant and soil chemical properties in a common garden plantation of the energy crop Populus.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 21;19(10):e0309321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309321. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39432492 Free PMC article.
-
Economic and Sustainability Impacts of Yield and Composition Variation in Bioenergy Crops: Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.).ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2024 Jan 22;12(5):1897-1910. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c05770. eCollection 2024 Feb 5. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2024. PMID: 38333206 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of methodologies used to determine aromatic lignin unit ratios in lignocellulosic biomass.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Mar 6;14(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13068-021-01897-y. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021. PMID: 33676549 Free PMC article.
-
Which Plant Traits Increase Soil Carbon Sequestration? Empirical Evidence From a Long-Term Poplar Genetic Diversity Trial.Glob Chang Biol. 2025 Sep;31(9):e70450. doi: 10.1111/gcb.70450. Glob Chang Biol. 2025. PMID: 40888515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sykes RW, Gjersing EL, Foutz K, Rottmann WH, Kuhn SA, Foster CE, et al. Down-regulation of p-coumaroyl quinate/shikimate 3′-hydroxylase (C3′H) and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) genes in the lignin biosynthetic pathway of Eucalyptus urophylla × E. grandis leads to improved sugar release. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015;8(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13068-015-0316-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Edmunds CW, Peralta P, Kelley SS, Chiang VL, Sharma-Shivappa RR, Davis MF, et al. Characterization and enzymatic hydrolysis of wood from transgenic Pinus taeda engineered with syringyl lignin or reduced lignin content. Cellulose. 2017;24(4):1901–1914. doi: 10.1007/s10570-017-1231-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

