Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
- PMID: 33676590
- PMCID: PMC8078879
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00099-0
Sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with severe or critical COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
Abstract
Background: Elevated proinflammatory cytokines are associated with greater COVID-19 severity. We aimed to assess safety and efficacy of sarilumab, an interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor, in patients with severe (requiring supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula or face mask) or critical (requiring greater supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal support) COVID-19.
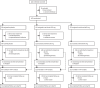
Methods: We did a 60-day, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational phase 3 trial at 45 hospitals in Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Chile, France, Germany, Israel, Italy, Japan, Russia, and Spain. We included adults (≥18 years) admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and pneumonia, who required oxygen supplementation or intensive care. Patients were randomly assigned (2:2:1 with permuted blocks of five) to receive intravenous sarilumab 400 mg, sarilumab 200 mg, or placebo. Patients, care providers, outcome assessors, and investigators remained masked to assigned intervention throughout the course of the study. The primary endpoint was time to clinical improvement of two or more points (seven point scale ranging from 1 [death] to 7 [discharged from hospital]) in the modified intention-to-treat population. The key secondary endpoint was proportion of patients alive at day 29. Safety outcomes included adverse events and laboratory assessments. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04327388; EudraCT, 2020-001162-12; and WHO, U1111-1249-6021.
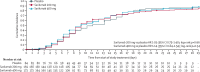
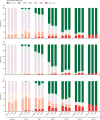
Findings: Between March 28 and July 3, 2020, of 431 patients who were screened, 420 patients were randomly assigned and 416 received placebo (n=84 [20%]), sarilumab 200 mg (n=159 [38%]), or sarilumab 400 mg (n=173 [42%]). At day 29, no significant differences were seen in median time to an improvement of two or more points between placebo (12·0 days [95% CI 9·0 to 15·0]) and sarilumab 200 mg (10·0 days [9·0 to 12·0]; hazard ratio [HR] 1·03 [95% CI 0·75 to 1·40]; log-rank p=0·96) or sarilumab 400 mg (10·0 days [9·0 to 13·0]; HR 1·14 [95% CI 0·84 to 1·54]; log-rank p=0·34), or in proportions of patients alive (77 [92%] of 84 patients in the placebo group; 143 [90%] of 159 patients in the sarilumab 200 mg group; difference -1·7 [-9·3 to 5·8]; p=0·63 vs placebo; and 159 [92%] of 173 patients in the sarilumab 400 mg group; difference 0·2 [-6·9 to 7·4]; p=0·85 vs placebo). At day 29, there were numerical, non-significant survival differences between sarilumab 400 mg (88%) and placebo (79%; difference +8·9% [95% CI -7·7 to 25·5]; p=0·25) for patients who had critical disease. No unexpected safety signals were seen. The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were 65% (55 of 84) in the placebo group, 65% (103 of 159) in the sarilumab 200 mg group, and 70% (121 of 173) in the sarilumab 400 mg group, and of those leading to death 11% (nine of 84) were in the placebo group, 11% (17 of 159) were in the sarilumab 200 mg group, and 10% (18 of 173) were in the sarilumab 400 mg group.
Interpretation: This trial did not show efficacy of sarilumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 and receiving supplemental oxygen. Adequately powered trials of targeted immunomodulatory therapies assessing survival as a primary endpoint are suggested in patients with critical COVID-19.
Funding: Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

