Multicenter evaluation of four immunoassays for the performance of early diagnosis of COVID-19 and assessment of antibody responses of patients with pneumonia in Taiwan
- PMID: 33676864
- PMCID: PMC7900773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.02.003
Multicenter evaluation of four immunoassays for the performance of early diagnosis of COVID-19 and assessment of antibody responses of patients with pneumonia in Taiwan
Abstract
Background/purpose: Our study goals were to evaluate the diagnostic performance of four anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies tests and the differences in dynamic immune responses between COVID-19 patients with and without pneumonia.
Methods: We collected 184 serum samples from 70 consecutively qRT-PCR-confirmed COVID-19 patients at four participating hospitals from 23 January 2020 to 30 September 2020. COVID-19 pneumonia was defined as the presence of new pulmonary infiltration. Serum samples were grouped by the duration after symptom onset on a weekly basis for antibody testing and analysis. The four immunoassays: Beckman SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM (Beckman Test), Siemens (ADVIA Centaur®) SARS-CoV-2 Total (COV2T) (Siemens Test), SBC COVID-19 IgG ELISA (SBC Test) and EliA SARS-CoV-2-Sp1 IgG/IgM/IgA P2 Research (EliA Test) were used for detecting the SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies.
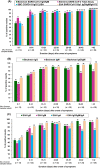
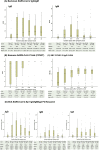
Results: The sensitivity of all tests reached 100% after 42 days of symptom onset. Siemens Test, the only test detecting total anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, had the best performance in the early diagnosis of COVID-19 infection (day 0-7: 77%; day 8-14: 95%) compared to the other 3 serological tests. All tests showed 100% specificity except SBC Test (98%). COVID-19 patients with pneumonia had significantly higher testing signal values than patients without pneumonia (all p values < 0.05, except EliA IgM Test). However, Siemens Test and SBC Test had highest probability in early prediction of the presence of COVID-19 pneumonia.
Conclusion: Chronological analysis of immune response among COVID-19 patients with different serological tests provides important information in the early diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and prediction of the risk of pneumonia after infection.
Keywords: Antibody responses; COVID-19; False positive; Immunoassays; Pneumonia.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical diagnostic performance evaluation of five immunoassays for antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis in a real-life routine care setting.Pan Afr Med J. 2021 May 3;39:3. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.39.3.26471. eCollection 2021. Pan Afr Med J. 2021. PMID: 34178231 Free PMC article.
-
Four point-of-care lateral flow immunoassays for diagnosis of COVID-19 and for assessing dynamics of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2.J Infect. 2020 Sep;81(3):435-442. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.06.023. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32553841 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 serological tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19 through the evaluation of three immunoassays: Two automated immunoassays (Euroimmun and Abbott) and one rapid lateral flow immunoassay (NG Biotech).J Clin Virol. 2020 Aug;129:104511. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104511. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32593133 Free PMC article.
-
Seropositivity rate and diagnostic accuracy of serological tests in 2019-nCoV cases: a pooled analysis of individual studies.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Oct;24(19):10208-10218. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23243. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33090430 Review.
-
Clinical applications of detecting IgG, IgM or IgA antibody for the diagnosis of COVID-19: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Mar;104:415-422. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.01.016. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33450372 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity and safety of homologous and heterologous ChAdOx1-S and mRNA-1273 vaccinations in healthy adults in Taiwan.J Clin Virol. 2022 Jun;150-151:105156. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105156. Epub 2022 Apr 6. J Clin Virol. 2022. PMID: 35413588 Free PMC article.
-
To PCR or not? The impact of shifting policy from PCR to rapid antigen tests to diagnose COVID-19 during the omicron epidemic: a nationwide surveillance study.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 20;11:1148637. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1148637. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37546311 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the sensitivity of antibody tests for the laboratory confirmation of COVID-19.Future Virol. 2021 Nov:10.2217/fvl-2021-0211. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2021-0211. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Future Virol. 2021. PMID: 34950219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State-wide random seroprevalence survey of SARS-CoV-2 past infection in a southern US State, 2020.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 27;17(4):e0267322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267322. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35476717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen S.Y., Lee Y.L., Lin Y.C., Lee N.Y., Liao C.H., Hung Y.P. Multicenter evaluation of two chemiluminescence and three lateral flow immunoassays for the diagnosis of COVID-19 and assessment of antibody dynamic responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Taiwan. Emerg Microb Infect. 2020;9(1):2157–2168. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

