Strategies for site-specific recombination with high efficiency and precise spatiotemporal resolution
- PMID: 33676891
- PMCID: PMC8050033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100509
Strategies for site-specific recombination with high efficiency and precise spatiotemporal resolution
Abstract
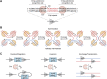
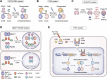
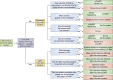
Site-specific recombinases (SSRs) are invaluable genome engineering tools that have enormously boosted our understanding of gene functions and cell lineage relationships in developmental biology, stem cell biology, regenerative medicine, and multiple diseases. However, the ever-increasing complexity of biomedical research requires the development of novel site-specific genetic recombination technologies that can manipulate genomic DNA with high efficiency and fine spatiotemporal control. Here, we review the latest innovative strategies of the commonly used Cre-loxP recombination system and its combinatorial strategies with other site-specific recombinase systems. We also highlight recent progress with a focus on the new generation of chemical- and light-inducible genetic systems and discuss the merits and limitations of each new and established system. Finally, we provide the future perspectives of combining various recombination systems or improving well-established site-specific genetic tools to achieve more efficient and precise spatiotemporal genetic manipulation.
Keywords: Cre-loxP; Dre-rox; gene manipulation; genome engineering; inducible; lineage tracing; optogenetics; photoactivatable; site-specific recombinase; site-specific recombination.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel Heterotypic Rox Sites for Combinatorial Dre Recombination Strategies.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Dec 29;6(3):559-71. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.025841. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26715092 Free PMC article.
-
Dre recombinase, like Cre, is a highly efficient site-specific recombinase in E. coli, mammalian cells and mice.Dis Model Mech. 2009 Sep-Oct;2(9-10):508-15. doi: 10.1242/dmm.003087. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Dis Model Mech. 2009. PMID: 19692579
-
Genetic lineage tracing with multiple DNA recombinases: A user's guide for conducting more precise cell fate mapping studies.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 8;295(19):6413-6424. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011631. Epub 2020 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32213599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-efficiency FLP and PhiC31 site-specific recombination in mammalian cells.PLoS One. 2007 Jan 17;2(1):e162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000162. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17225864 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian genome targeting using site-specific recombinases.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:1108-36. doi: 10.2741/1867. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146801 Review.
Cited by
-
Different pieces of the same puzzle: a multifaceted perspective on the complex biological basis of Parkinson's disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023 Jul 13;9(1):110. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00535-8. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023. PMID: 37443150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral vector-mediated transgene delivery with novel recombinase systems for targeting neuronal populations defined by multiple features.Neuron. 2024 Jan 3;112(1):56-72.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.09.038. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 37909037 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Cre/lox71-Based System for Inducible Expression of Recombinant Proteins and Genome Editing.Cells. 2022 Jul 7;11(14):2141. doi: 10.3390/cells11142141. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883584 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges Facing CRISPR/Cas9-Based Genome Editing in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 18;13:902413. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.902413. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35677236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tools for Cre-Mediated Conditional Deletion of Floxed Alleles from Developing Cerebellar Purkinje Cells.eNeuro. 2024 Jun 3;11(6):ENEURO.0149-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0149-24.2024. Print 2024 Jun. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 38777609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagy A. Cre recombinase: The universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis. 2000;26:99–109. - PubMed
-
- Kawano F., Okazaki R., Yazawa M., Sato M. A photoactivatable Cre-loxP recombination system for optogenetic genome engineering. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016;12:1059–1064. - PubMed
-
- Lewandoski M. Conditional control of gene expression in the mouse. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001;2:743–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

