The phosphorylation of the Smad2/3 linker region by nemo-like kinase regulates TGF-β signaling
- PMID: 33676893
- PMCID: PMC8047224
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100512
The phosphorylation of the Smad2/3 linker region by nemo-like kinase regulates TGF-β signaling
Abstract
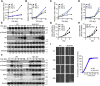
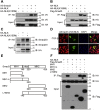
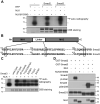
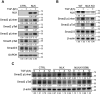
Smad2 and Smad3 (Smad2/3) are structurally similar proteins that primarily mediate the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling responsible for driving cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration. The dynamics of the Smad2/3 phosphorylation provide the key mechanism for regulating the TGF-β signaling pathway, but the details surrounding this phosphorylation remain unclear. Here, using in vitro kinase assay coupled with mass spectrometry, we identified for the first time that nemo-like kinase (NLK) regulates TGF-β signaling via modulation of Smad2/3 phosphorylation in the linker region. TGF-β-mediated transcriptional and cellular responses are suppressed by NLK overexpression, whereas NLK depletion exerts opposite effects. Specifically, we discovered that NLK associates with Smad3 and phosphorylates the designated serine residues located in the linker region of Smad2 and Smad3, which inhibits phosphorylation at the C terminus, thereby decreasing the duration of TGF-β signaling. Overall, this work demonstrates that phosphorylation on the linker region of Smad2/3 by NLK counteracts the canonical phosphorylation in response to TGF-β signals, thus providing new insight into the mechanisms governing TGF-β signaling transduction.
Keywords: NLK; Smad2; Smad3; TGF-β signaling; linker phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small C-terminal domain phosphatases dephosphorylate the regulatory linker regions of Smad2 and Smad3 to enhance transforming growth factor-beta signaling.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 15;281(50):38365-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607246200. Epub 2006 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17035229
-
Transforming growth factor-β signalling: role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2017-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770288 Review.
-
Interleukin 1 β-induced SMAD2/3 linker modifications are TAK1 dependent and delay TGFβ signaling in primary human mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Signal. 2017 Dec;40:190-199. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.09.010. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 28943409
-
Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylated at both linker and COOH-terminal regions transmit malignant TGF-beta signal in later stages of human colorectal cancer.Cancer Res. 2009 Jul 1;69(13):5321-30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4203. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19531654
-
A tale of two proteins: differential roles and regulation of Smad2 and Smad3 in TGF-beta signaling.J Cell Biochem. 2007 May 1;101(1):9-33. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21255. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17340614 Review.
Cited by
-
Limb expression 1-like protein promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance via nucleolin-mediated ribosomal RNA synthesis in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2023 Apr;114(4):1740-1756. doi: 10.1111/cas.15687. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36478492 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective use of amniotic mesenchymal stem cell metabolite products for tissue regeneration.J Biol Eng. 2023 Feb 9;17(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13036-023-00331-1. J Biol Eng. 2023. PMID: 36759827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein phosphatase 6 promotes transforming growth factor-β signaling in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 Dec 19;85(12):1319-1323. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0380. Epub 2023 Oct 25. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37880139 Free PMC article.
-
M2 macrophage-derived exosomes reverse TGF-β1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transformation in BEAS-2B cells via the TGF-βRI/Smad2/3 signaling pathway.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 11;30(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02516-4. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40211426 Free PMC article.
-
Interrelation of Natural Polyphenol and Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy.Molecules. 2024 Dec 25;30(1):20. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010020. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39795078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

