Systematic Review of the Long-Term Effects of Presurgical Orthopedic Devices on Patient Outcomes
- PMID: 33678051
- PMCID: PMC8750140
- DOI: 10.1177/1055665621998176
Systematic Review of the Long-Term Effects of Presurgical Orthopedic Devices on Patient Outcomes
Abstract
Objective: To perform a systematic review of the literature to identify the long-term effects of presurgical orthopedic (PSO) device use on patient outcomes.
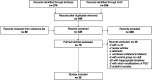
Design: A comprehensive literature review of Embase and Ovid databases was performed to identify all English-language publications related to unilateral cleft lip and palate, presurgical devices, and patient outcomes. Studies were excluded if they did not report patient outcomes beyond 2 years of age, did not describe the use of a PSO device, were case reports (n < 10), or were purely descriptive studies.
Main outcome measures: Reported patient outcomes following the use of PSO devices.
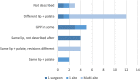
Results: Following a review of all articles by 2 independent reviews, 30 articles were selected for inclusion. Overall, there was no reported consensus as to the long-term effects of PSO devices. Furthermore, this study identified that only 10% of published research controlled for confounding factors that could influence the reported results. Confounding factors that were identified included different operating surgeon, different surgical protocols, and different rates of revision surgeries.
Conclusions: Overall, this systematic review identified 2 important conclusions. Firstly, there is no consensus in the literature about the long-term effects of PSO devices on long-term patient outcomes. Secondly, research in this domain is limited by confounding factors that influence the applicability of the reported results.
Keywords: cleft palate; growth; nasolabial aesthetics; occlusion; outcomes; presurgical orthopedic devices.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Adali N, Mars M, Petrie A, Noar J, Sommerlad B. Presurgical orthopedics has no effect on archform in unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2012;49(1):5–13. doi:10.1597/11-030 - PubMed
-
- Asher-McDade C, Brattström V, Dahl E, McWilliam J, Mølsted K, Plint DA, Prahl-Andersen B, Semb G, Shaw WC, The RP. A six-center international study of treatment outcome in patients with clefts of the lip and palate: part 4. Assessment of nasolabial appearance. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1992;29(5):409–412. doi:10.1597/1545-1569_1992_029_0409_asciso_2.3.co_2 - PubMed
-
- Bardach J, Morris HL, Olin WH. Late results of primary veloplasty: the Marburg Project. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;73(2):207–218. doi:10.1097/00006534-198402000-00007 - PubMed
-
- Barillas I, Dec W, Warren SM, Cutting CB, Grayson BH. Nasoalveolar molding improves long-term nasal symmetry in complete unilateral cleft lip-cleft palate patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123(3):1002–1006. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e318199f46e - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical