The prohibitins (PHB) gene family in tomato: Bioinformatic identification and expression analysis under abiotic and phytohormone stresses
- PMID: 33678114
- PMCID: PMC8820253
- DOI: 10.1080/21645698.2021.1872333
The prohibitins (PHB) gene family in tomato: Bioinformatic identification and expression analysis under abiotic and phytohormone stresses
Abstract
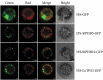
The prohibitins (PHB) are SPFH domain-containing proteins found in the prokaryotes to eukaryotes. The plant PHBs are associated with a wide range of biological processes, including senescence, development, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. The PHB proteins are identified and characterized in the number of plant species, such as Arabidopsis, rice, maize, and soybean. However, no systematic identification of PHB proteins was performed in Solanum lycopersicum. In this study, we identified 16 PHB proteins in the tomato genome. The analysis of conserved motifs and gene structure validated the phylogenetic classification of tomato PHB proteins. It was observed that various members of tomato PHB proteins undergo purifying selection based on the Ka/Ks ratio and are targeted by four families of miRNAs. Moreover, SlPHB proteins displayed a very unique expression pattern in different plant parts including fruits at various development stages. It was found that SlPHBs processed various development-related and phytohormone responsive cis-regulatory elements in their promoter regions. Furthermore, the exogenous phytohormones treatments (Abscisic acid, indole-3-acetic acid, gibberellic acid, methyl jasmonate) salt and drought stresses induce the expression of SlPHB. Moreover, the subcellular localization assay revealed that SlPHB5 and SlPHB10 were located in the mitochondria. This study systematically summarized the general characterization of SlPHBs in the tomato genome and provides a foundation for the functional characterization of PHB genes in tomato and other plant species.
Keywords: Tomato; expression; phylogeny; prohibitins; stress; synteny.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The DUF221 domain-containing (DDP) genes identification and expression analysis in tomato under abiotic and phytohormone stress.GM Crops Food. 2021 Jan 2;12(1):586-599. doi: 10.1080/21645698.2021.1962207. Epub 2021 Aug 11. GM Crops Food. 2021. PMID: 34379048 Free PMC article.
-
The Characteristics and Expression Analysis of the Tomato SlRBOH Gene Family under Exogenous Phytohormone Treatments and Abiotic Stresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 26;25(11):5780. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115780. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891968 Free PMC article.
-
The LEA gene family in tomato and its wild relatives: genome-wide identification, structural characterization, expression profiling, and role of SlLEA6 in drought stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Dec 19;22(1):596. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03953-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36536303 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of NAC Genes Reveals Differential Expression Patterns in Response to Pst DC3000 and Their Overlapping Expression Pattern during PTI and ETI in Tomato.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 2;13(11):2015. doi: 10.3390/genes13112015. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the WD40 Gene Family in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.).Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 15;14(6):1273. doi: 10.3390/genes14061273. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, structural characterization and gene expression analysis of the WRKY transcription factor family in pea (Pisum sativum L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Feb 16;24(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04774-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38365619 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Drought-Responsive Functional Analysis of the GST Gene Family in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.).Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;14(2):239. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020239. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002423 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Evolution, and Expression Patterns of the Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase Gene Family in Saccharum Species.Plants (Basel). 2025 Aug 6;14(15):2433. doi: 10.3390/plants14152433. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805782 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression pattern analysis of the GATA gene family in Sorghum bicolor.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 4;14:1163357. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1163357. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37600205 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
