Effects of Tigecycline Combined with Azithromycin Against Biofilms of Multidrug-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates from a Patient in China
- PMID: 33679134
- PMCID: PMC7924117
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S298274
Effects of Tigecycline Combined with Azithromycin Against Biofilms of Multidrug-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates from a Patient in China
Abstract
Purpose: Our aim was to investigate in vitro biofilm formation by S. maltophilia and the effects of antibacterial agents used to prevent biofilm formation.
Methods: Two trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole-resistant S. maltophilia strains were isolated from the pleural effusion of a patient with cancer. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of amikacin, azithromycin, cefoperazone/sulbactam, and tigecycline were determined. The checkerboard method was used to determine the fractional inhibitory concentration indices (FICIs). A crystal violet biofilm assay and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) were used to observe biofilm formation. In vitro effects of azithromycin combined with tigecycline on biofilms of S. maltophilia strains were tested.
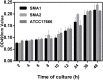
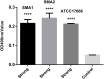
Results: The two S. maltophilia isolates were confirmed to produce strong biofilms. Crystal violet biofilm assay and CLSM analysis of S. maltophilia biofilm were in the initial adhesive stage after 2 h incubation. Biofilm was in the exponential phase of growth at 12 h and reached maximal growth at 36-48 h. Compared with tigecycline or azithromycin alone, the combination of tigecycline and azithromycin increased the inhibiting effect S. maltophilia biofilm biomass after incubation for 12 h. Compared with the control group, in almost all strains treated with tigecycline and azithromycin, the biofilm was significantly suppressed significance (P<0.001). We found that 2x MIC azithromycin combined with 1x MIC tigecycline had the best inhibiting effect against the biofilm, the biofilm inhibition rates of three strains were all over 60%, the biofilm thickness was inhibited from 36.00 ± 4.00 μm to 8.00 μm, from 40.00 μm to 6.67± 2.31 μm, and from 32.00 μm to 13.33 ± 2.31 μm in SMA1, SMA2 and ATCC17666, respectively.
Conclusion: Azithromycin combined with tigecycline inhibited biofilm formation by S. maltophilia. Our study provides an experimental basis for a possible optimal treatment strategy for S. maltophilia biofilm-related infections.
Keywords: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; azithromycin; biofilm; tigecycline; trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.
© 2021 Yue et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


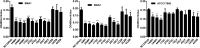

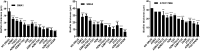

Similar articles
-
Effects of Fluoroquinolones and Azithromycin on Biofilm Formation of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 13;6:29701. doi: 10.1038/srep29701. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27405358 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activities of antimicrobial combinations against planktonic and biofilm forms of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1186669. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1186669. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37408643 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole (SXT), Minocycline, Tigecycline, Moxifloxacin, and Ceftazidime Alone and in Combinations for SXT-Susceptible and SXT-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia by In Vitro Time-Kill Experiments.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 21;11(3):e0152132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152132. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26999818 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro combination of tigecycline with other antibiotics in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates.Turk J Med Sci. 2019 Apr 18;49(2):683-686. doi: 10.3906/sag-1808-55. Turk J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30866602 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of antimicrobials on Stenotrophomonas maltophilia biofilm.Future Microbiol. 2021 Jan;16(2):83-93. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2020-0115. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Future Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33470844
Cited by
-
The Relationship between the Biofilm Genes and Antibiotic Resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.Int J Microbiol. 2023 Aug 31;2023:8873948. doi: 10.1155/2023/8873948. eCollection 2023. Int J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37692920 Free PMC article.
-
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia in adult patients with hematological diseases: clinical characteristics and risk factors for 28-day mortality.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jan 7;13(1):e0101124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01011-24. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39611832 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tigecycline combined with Cefoperazone on bacterial clearance and serum biochemical indexes in patients with pulmonary infections in ICU.Pak J Med Sci. 2022 Jul-Aug;38(6):1622-1626. doi: 10.12669/pjms.38.6.5872. Pak J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35991266 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognosis of Patients Tested Positive for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia from Different Sources.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Jul 24;16:4779-4787. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S417151. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37520451 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro synergy screens of FDA-approved drugs reveal novel zidovudine- and azithromycin-based combinations with last-line antibiotics against Klebsiella pneumoniae.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 2;13(1):14429. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39647-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37660210 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

