Effects of Recombinant Angiogenin on Collagen Fiber Formation and Angiogenesis in the Dermis of Wistar Rats
- PMID: 33679135
- PMCID: PMC7926187
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S294825
Effects of Recombinant Angiogenin on Collagen Fiber Formation and Angiogenesis in the Dermis of Wistar Rats
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to assess the capability of recombinant angiogenin isolated from Pichia pastoris yeasts to stimulate regenerative processes in the dermis of experimental animals.
Patients and methods: Wistar rats were administered with recombinant angiogenin intracutaneously. Morphological examination of the skin and the assessment of the proliferative activity of the epidermal cells were carried out. Additionally, cytokine production by human whole blood cells exposed to angiogenin was analyzed ex vivo.
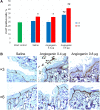
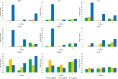
Results: Administration of angiogenin stimulates collagen fiber formation and angiogenesis. This stimulation is tightly associated with an increase in the number of fibroblasts, an increased numerical density of dermal blood vessels and an increased density of collagen fibers; also, it activates the proliferation of basal cells. Angiogenin induces the production of MCP, IL-8, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-10, TGF-β, and VEGF by blood cells.
Conclusion: The results obtained indicate a broad spectrum of actions of recombinant angiogenin during regenerative processes in the basal layer of the dermis.
Keywords: cytokines; intracutaneous injections; pathomorphological analysis; regeneration.
© 2021 Yurina et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
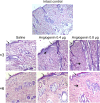
 Expansion of the stratum corneum,
Expansion of the stratum corneum,  an increase in the number of epidermal layers,
an increase in the number of epidermal layers,  thickened collagen fibers,
thickened collagen fibers,  the site of newly formed collagen with proliferating fibroblasts (the edge of the injection area). Hematoxylin/eosin staining, 100× magnification.
the site of newly formed collagen with proliferating fibroblasts (the edge of the injection area). Hematoxylin/eosin staining, 100× magnification.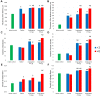
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

