Renoprotective effects of cinnamon oil against APAP-Induced nephrotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation in rats
- PMID: 33679180
- PMCID: PMC7910143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.01.002
Renoprotective effects of cinnamon oil against APAP-Induced nephrotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation in rats
Abstract
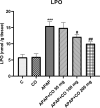
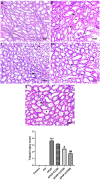
Acetaminophen (APAP) is used as a primary medication in relieving moderate pain and fever. However, APAP is associated with toxic effects in renal tissue that appear because of its free radicals property. The principle goal of the present work is to assess the kidney damage by APAP and its restore antioxidative property of cinnamon oil (CO). Animals were distributed into six animals each in six groups. Rats were administered with three varying doses of CO from 50 to 200 mg/kg b.w. respectively and only a single dose of APAP. APAP induced an alteration in serum biochemical markers, imbalance in oxidative parameters, morphological changes in kidney tissue along with increased interleukins cytokines (IL-1β & 6) and caspase (3, 9) levels. CO administration significantly ameliorates all the parameters and histopathological changes were restored. Moreover, it also restored the activities of antioxidative enzymes. Our work proved that an variance of oxidative markers in the kidney by APAP is ameliorated by CO in rats. Thus, CO could be used in reducing APAP-induced nephrotoxicity.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; Caspases-3, 9; Cinnamon oil; Inflammation; Nephrotoxicity; Oxidative stress.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

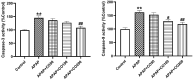
References
-
- Abdul R.A., Gopalakrishnan G., Venkatesan P. Isolation and identification of mosquito larvicidal compound from Abutilon indicum (Linn.). Sweet. Parasitol. Res. 2008;102(5):981–988. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S.T., Arjumand W., Nafees S., Seth A., Ali N., Rashid S., Sultana S. Hesperidin alleviates acetaminophen induced toxicity in Wistar rats by abrogation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Toxicol. Lett. 2012;208:149–161. - PubMed
-
- Ajami M., Eghtesadi S., Pazoki-Toroudi H., Habibey R., Ebrahimi S.A. Effect of Crocus sativus on gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity. Biol. Res. 2010;43:83–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

