Bibliometric analysis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) literature published in Web of Science 2019-2020
- PMID: 33679183
- PMCID: PMC7927969
- DOI: 10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_332_20
Bibliometric analysis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) literature published in Web of Science 2019-2020
Abstract
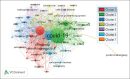
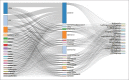
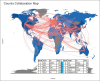
Coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China, turned into a pandemic in record time. Communication of disease presentation and mechanism of spread remain keys to getting ahead of the virus and limiting its spread beyond the capacity of management. Owing to huge academic focus and pandemic concern around the globe, this bibliometric analysis investigated research productivity related to coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic using the Web of Science database. The relevant data were harvested, and search query was further refined by publication years (2020 OR 2019) and document types (article, book chapter, and proceedings paper). Finally, 6694 records were imported and downloaded in Plaintext and BibTeX formats on August 1, 2020. The data analysis was performed using MS Excel, VOS viewer, and Biblioshiny software. Of the 6694 publications that appeared in that period, the USA and Chinese research institutions topped the numbers. At the same time, the Journal of Medical Virology and CUREUS (Cureus Journal of Medical Science), remained favorite journals for publications. The pattern of multi-author publications has outstripped that of single-authors. Apart from COVID-19 and the novel coronavirus, the important keywords mentioned included pandemic, pneumonia, epidemiology, public health, outbreak, epidemic, China, infection, and treatment. The analysis shows a strong local research response from China, with large teams reporting on the disease outbreak. Subsequent studies will document a global response as the virus spreads worldwide. The initial research related to the current coronavirus outbreak was reported from within China. The data and patterns were supposed to alter as the virus spread globally.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; COVID-19; China; bibliometric; bibliometric-coronavirus; health care; pandemic; research productivity; severe acute respiratory syndrome-cov-2; the World Health Organization.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Family and Community Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global Maps of Avian Leukosis Viruses: Research Trends and Themes Based on Networking.Vet Sci. 2022 Dec 26;10(1):16. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10010016. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36669017 Free PMC article.
-
Scars of COVID-19: A bibliometric analysis of post-COVID-19 fibrosis.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 20;10:967829. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.967829. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36203683 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer of publications on COVID-19.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jul;8(13):816. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4235. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32793661 Free PMC article.
-
A Worldwide Bibliometric Analysis of Publications on Coronavirus in the Past 3 Decades: A Bibliometric Article.Iran J Public Health. 2021 Dec;50(12):2374-2383. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v50i12.7921. Iran J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 36317024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019: A new severe acute respiratory syndrome from Wuhan in China.Acta Virol. 2020;64(2):245-250. doi: 10.4149/av_2020_201. Acta Virol. 2020. PMID: 32551792 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling COVID-19 Transmission Dynamics: A Bibliometric Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 29;19(21):14143. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114143. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36361019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global Maps of Avian Leukosis Viruses: Research Trends and Themes Based on Networking.Vet Sci. 2022 Dec 26;10(1):16. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10010016. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36669017 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation of libraries during Covid-19 pandemic: A systematic review.Journal of academic librarianship. 2022 Jul;48(4):102534. doi: 10.1016/j.acalib.2022.102534. Epub 2022 Apr 28. 2022. PMID: 35502415 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing knowledge entities about COVID-19 using entitymetrics.Scientometrics. 2021;126(5):4491-4509. doi: 10.1007/s11192-021-03933-y. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Scientometrics. 2021. PMID: 33746309 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Scientific Contributions of Nepal on COVID-19.Curr Trop Med Rep. 2021;8(4):257-264. doi: 10.1007/s40475-021-00247-0. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Curr Trop Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34745841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang HJ, Du SH, Yue X, Chen CX. Review and prospect of pathological features of corona virus disease. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;36:16–20. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources