Incidental Gallbladder Carcinoma in Gallbladder Polyps: Challenges of Gallbladder Malignancy for an Endemic Population
- PMID: 33679217
- PMCID: PMC7909354
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms2021.28.1.4
Incidental Gallbladder Carcinoma in Gallbladder Polyps: Challenges of Gallbladder Malignancy for an Endemic Population
Abstract
Background: Gallbladder polyps are considered pre-malignant lesions of gallbladder carcinoma. This study aims to highlight the role of early cholecystectomy in the management of gallbladder polyps in an endemic population.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 2,076 lap cholecystectomy procedures performed at the Department of Surgical Gastroenterology at a tertiary referral centre in Northern India was conducted and incidental malignancy in gallbladder polyps analysed. The 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer for tumour-node-metastasis (TNM) staging of gallbladder carcinoma was used.
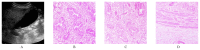
Results: Of 54 patients with gallbladder polyps, 53 had benign histology and one had malignant cells in the lamina propria suggestive of T1a adenocarcinoma. The patient with the malignant polyp was older (57 years old) than the patients in the non-cancer group, which had a mean age of 45 (P = 0.039). The size of the malignant polyp was approximately 4 mm, significantly smaller than the average 7.9 mm size of the benign polys (P = 0.031).
Conclusion: Cholecystectomy needs to be considered early in the management of small-sized gallbladder polyps, particularly in areas endemic for gallbladder carcinoma.
Keywords: endemic area; gallbladder carcinoma; gallbladder polyp; size.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
