Ginkgolide B Maintains Calcium Homeostasis in Hypoxic Hippocampal Neurons by Inhibiting Calcium Influx and Intracellular Calcium Release
- PMID: 33679323
- PMCID: PMC7928385
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2020.627846
Ginkgolide B Maintains Calcium Homeostasis in Hypoxic Hippocampal Neurons by Inhibiting Calcium Influx and Intracellular Calcium Release
Abstract
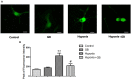
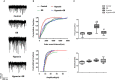
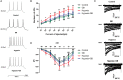
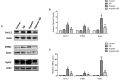
Ginkgolide B (GB), a terpene lactone and active ingredient of Ginkgo biloba, shows protective effects in neuronal cells subjected to hypoxia. We investigated whether GB might protect neurons from hypoxic injury through regulation of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis. Primary hippocampal neurons subjected to chemical hypoxia (0.7 mM CoCl2) in vitro exhibited an increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ (measured from the fluorescence of fluo-4), but this effect was significantly diminished by pre-treatment with 0.4 mM GB. Electrophysiological recordings from the brain slices of rats exposed to hypoxia in vivo revealed increases in spontaneous discharge frequency, action potential frequency and calcium current magnitude, and all these effects of hypoxia were suppressed by pre-treatment with 12 mg/kg GB. Western blot analysis demonstrated that hypoxia was associated with enhanced mRNA and protein expressions of Cav1.2 (a voltage-gated Ca2+ channel), STIM1 (a regulator of store-operated Ca2+ entry) and RyR2 (isoforms of Ryanodine Receptor which mediates sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release), and these actions of hypoxia were suppressed by GB. Taken together, our in vitro and in vivo data suggest that GB might protect neurons from hypoxia, in part, by regulating Ca2+ influx and intracellular Ca2+ release to maintain Ca2+ homeostasis.
Keywords: cytoplasmic calcium; ginkgolide B; homeostasis; hypoxia; neuron.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Lei, Zhao, Xu, Dong, Ran, Shi and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Trimetazidine protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced injury through ameliorates calcium homeostasis.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Jul 5;236:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 May 1. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25937560
-
Oral administration of Ginkgolide B alleviates hypoxia-induced neuronal damage in rat hippocampus by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Feb;22(2):140-145. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.26228.6569. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30834078 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide B, a constituent of Ginkgo biloba, facilitates glutamate exocytosis from rat hippocampal nerve terminals.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 May 9;514(2-3):141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.03.027. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15910800
-
Remodeling of Intracellular Ca2+ Homeostasis in Rat Hippocampal Neurons Aged In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 24;21(4):1549. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041549. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32102482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological studies supporting the therapeutic use of Ginkgo biloba extract for Alzheimer's disease.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003 Jun;36 Suppl 1:S8-14. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40454. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 13130383 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential role and therapeutic implications of glutathione peroxidase 4 in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Mar 1;20(3):613-631. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01343. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38886929 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide B as a biopsychosocial treatment salvages repeated restraint stress-induced amygdalar anomalies in mice.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Dec 18;18:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.12.010. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39844942 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis and Alzheimer's: unveiling new avenues for the treatment and prevention.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Apr 1;40(4):167. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01587-w. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40167846 Review.
-
From traditional medicine to nanomedicine: potential of Ginkgo biloba extracts in treating inflammatory skin diseases.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Jun 11;15(8):2643-2656. doi: 10.1039/d4md00194j. eCollection 2024 Aug 14. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39149101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginkgo biloba: A Leaf of Hope in the Fight against Alzheimer's Dementia: Clinical Trial Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 27;13(6):651. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060651. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Campos-Toimil M., Lugnier C., Droy-Lefaix M. T., Takeda K. (2000). Inhibition of type 4 phosphodiesterase by rolipram and Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) decreases agonist-induced rises in internal calcium in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20, E34–E40. 10.1161/01.ATV.20.9.e34 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

