Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1) as a Novel Regulator of Early Astroglial Differentiation
- PMID: 33679332
- PMCID: PMC7930235
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.642521
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1) as a Novel Regulator of Early Astroglial Differentiation
Abstract
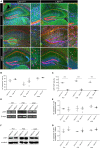
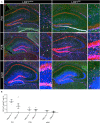
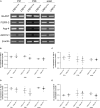
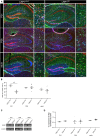
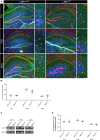
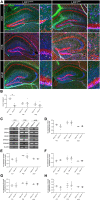
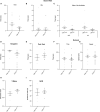
Astrocytes are the most abundant cell type within the central nervous system (CNS) with various functions. Furthermore, astrocytes show a regional and developmental heterogeneity traceable with specific markers. In this study, the influence of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) on astrocytic maturation within the hippocampus was analyzed during development. Previous studies mostly focused on the involvement of LRP1 in the neuronal compartment, where the deletion caused hyperactivity and motor dysfunctions in knockout animals. However, the influence of LRP1 on glia cells is less intensively investigated. Therefore, we used a newly generated mouse model, where LRP1 is specifically deleted from GLAST-positive astrocytes co-localized with the expression of the reporter tdTomato to visualize recombination and knockout events in vivo. The influence of LRP1 on the maturation of hippocampal astrocytes was assessed with immunohistochemical stainings against stage-specific markers as well as on mRNA level with RT-PCR analysis. The examination revealed that the knockout induction caused a significantly decreased number of mature astrocytes at an early developmental timepoint compared to control animals. Additionally, the delayed maturation of astrocytes also caused a reduced activity of neurons within the hippocampus. As previous studies showed that the glial specification and maturation of astrocytes is dependent on the signaling cascades Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk and PI3K/Akt, the phosphorylation of the signaling molecules Erk1/2 and Akt was analyzed. The hippocampal tissue of LRP1-deficient animals at P21 showed a significantly decreased amount of activated Erk in comparison to control tissue leading to the conclusion that the activation of this signaling cascade is dependent on LRP1 in astrocytes, which in turn is necessary for proper maturation of astrocytes. Our results showed that the deletion of LRP1 at an early developmental timepoint caused a delayed maturation of astrocytes in the hippocampus based on an altered activation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk signaling pathway. However, with ongoing development these effects were compensated and the number of mature astrocytes was comparable as well as the activity of neurons. Therefore, LRP1 acts as an early regulator of the differentiation and maturation of astrocytes within the hippocampus.
Keywords: LRP1; astrocyte functions; astrocyte heterogeneity; differentiation; hippocampus; in vivo knockout model.
Copyright © 2021 Romeo, Boden-El Mourabit, Scheller, Mark and Faissner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deletion of LRP1 From Astrocytes Modifies Neuronal Network Activity in an in vitro Model of the Tripartite Synapse.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Jan 14;14:567253. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.567253. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33519378 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 is a novel modulator of radial glia stem cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.Glia. 2016 Aug;64(8):1363-80. doi: 10.1002/glia.23009. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Glia. 2016. PMID: 27258849 Free PMC article.
-
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway is involved in regulating low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1-mediated β-amyloid protein internalization in mouse brain.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Jul;76:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.04.019. Epub 2016 May 6. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27163530
-
Cross-talk signals in the CNS: role of neurotrophic and hormonal factors, adhesion molecules and intercellular signaling agents in luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH)-astroglial interactive network.Front Biosci. 1997 Mar 1;2:d88-125. doi: 10.2741/a177. Front Biosci. 1997. PMID: 9159216 Review.
-
The LHRH-astroglial network of signals as a model to study neuroimmune interactions: assessment of messenger systems and transduction mechanisms at cellular and molecular levels.Neuroimmunomodulation. 1996 Jan-Feb;3(1):1-27. doi: 10.1159/000097223. Neuroimmunomodulation. 1996. PMID: 8892357 Review.
Cited by
-
Amyloid-β oligomers increase the binding and internalization of tau oligomers in human synapses.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Dec 17;149(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02839-2. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 39688618 Free PMC article.
-
The duality of amyloid-β: its role in normal and Alzheimer's disease states.Mol Brain. 2024 Jul 17;17(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01118-1. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 39020435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1) in the glial lineage modulates neuronal excitability.Front Netw Physiol. 2023 Jun 13;3:1190240. doi: 10.3389/fnetp.2023.1190240. eCollection 2023. Front Netw Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37383546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of furin in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric diseases.Transl Neurodegener. 2022 Aug 23;11(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00313-1. Transl Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35996194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated expression of cholesterol transporter LRP-1 is crucially implicated in the pathobiology of glioblastoma.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 4;13:1003730. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1003730. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36267880 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

