No Impact of Stochastic Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation on Arterial Pressure and Heart Rate Variability in the Elderly Population
- PMID: 33679355
- PMCID: PMC7925407
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.646127
No Impact of Stochastic Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation on Arterial Pressure and Heart Rate Variability in the Elderly Population
Abstract
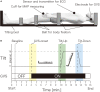
Objective: Noisy galvanic vestibular stimulation (nGVS) is often used to improve postural stability in disorders, such as neurorehabilitation montage. For the safe use of nGVS, we investigated whether arterial pressure (AP) and heart rate vary during static supine and slow whole-body tilt with random nGVS (0.4 mA, 0.1-640 Hz, gaussian distribution) in a healthy elderly population.
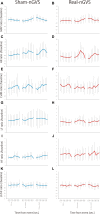
Methods: This study was conducted with a double-blind, sham-controlled, cross-over design. Seventeen healthy older adults were recruited. They were asked to maintain a static supine position on a bed for 10 min, and the bed was tilted up (TU) to 70 degrees within 30 s. After maintaining this position for 3 min, the bed was passively tilted down (TD) within 30 s. Real-nGVS or sham-nGVS was applied from 4 to 15 min. The time course of mean arterial pressure (MAP) and RR interval variability (RRIV) were analyzed to estimate the autonomic nervous activity.
Result: nGVS and/or time, including pre-/post-event (nGVS-start, TU, and TD), had no impact on MAP and RRIV-related parameters. Further, there was no evidence supporting the argument that nGVS induces pain, vertigo/dizziness, and uncomfortable feeling.
Conclusion: nGVS may not affect the AP and RRIV during static position and whole-body tilting or cause pain, vertigo/dizziness, and discomfort in the elderly.
Keywords: RR interval variability; arterial pressure; galvanic vestibular stimulation; heart rate variability; stochastic resonance; whole-body tilting.
Copyright © 2021 Matsugi, Nagino, Shiozaki, Okada, Mori, Nakamura, Douchi, Oku, Nagano and Tamaru.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scoping out noisy galvanic vestibular stimulation: a review of the parameters used to improve postural control.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 2;17:1156796. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1156796. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37205050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Different Stimulation Conditions on the Stimulation Effect of Noisy Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Sep 24;14:581405. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.581405. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33192415 Free PMC article.
-
Noisy Galvanic Stimulation Improves Roll-Tilt Vestibular Perception in Healthy Subjects.Front Neurol. 2018 Mar 1;9:83. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00083. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29545766 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Noisy Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation Change Vestibulospinal Function.Front Neurosci. 2020 Apr 28;14:388. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00388. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32410952 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of nGVS to improve postural stability in people with bilateral vestibulopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 28;16:1010239. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1010239. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36248647 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Scoping out noisy galvanic vestibular stimulation: a review of the parameters used to improve postural control.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 2;17:1156796. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1156796. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37205050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of continuous supplementation of Acanthopanax senticosus Harms on the cardiac autonomic function of community-dwelling elderly individuals during resting and standing tests: a randomized controlled trial.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Mar 8;11:1336676. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1336676. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38525193 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Pressure Variability and Ocular Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials Are Independently Associated With Orthostatic Hypotension.J Clin Neurol. 2024 Nov;20(6):571-579. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2024.0092. J Clin Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39505309 Free PMC article.
-
Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex Is Modulated by Noisy Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation.Front Neurol. 2022 Feb 17;13:826739. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.826739. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35250830 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

