Phenotypic Characterization and Brain Structure Analysis of Calcium Channel Subunit α2δ-2 Mutant (Ducky) and α2δ Double Knockout Mice
- PMID: 33679366
- PMCID: PMC7933509
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsyn.2021.634412
Phenotypic Characterization and Brain Structure Analysis of Calcium Channel Subunit α2δ-2 Mutant (Ducky) and α2δ Double Knockout Mice
Abstract
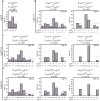
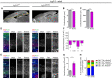
Auxiliary α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels modulate channel trafficking, current properties, and synapse formation. Three of the four isoforms (α2δ-1, α2δ-2, and α2δ-3) are abundantly expressed in the brain; however, of the available knockout models, only α2δ-2 knockout or mutant mice display an obvious abnormal neurological phenotype. Thus, we hypothesize that the neuronal α2δ isoforms may have partially specific as well as redundant functions. To address this, we generated three distinct α2δ double knockout mouse models by crossbreeding single knockout (α2δ-1 and -3) or mutant (α2δ-2/ducky) mice. Here, we provide a first phenotypic description and brain structure analysis. We found that genotypic distribution of neonatal litters in distinct α2δ-1/-2, α2δ-1/-3, and α2δ-2/-3 breeding combinations did not conform to Mendel's law, suggesting premature lethality of single and double knockout mice. Notably, high occurrences of infant mortality correlated with the absence of specific α2δ isoforms (α2Δ-2 > α2δ-1 > α2δ-3), and was particularly observed in cages with behaviorally abnormal parenting animals of α2δ-2/-3 cross-breedings. Juvenile α2δ-1/-2 and α2δ-2/-3 double knockout mice displayed a waddling gate similar to ducky mice. However, in contrast to ducky and α2δ-1/-3 double knockout animals, α2δ-1/-2 and α2δ-2/-3 double knockout mice showed a more severe disease progression and highly impaired development. The observed phenotypes within the individual mouse lines may be linked to differences in the volume of specific brain regions. Reduced cortical volume in ducky mice, for example, was associated with a progressively decreased space between neurons, suggesting a reduction of total synaptic connections. Taken together, our findings show that α2δ subunits differentially regulate premature survival, postnatal growth, brain development, and behavior, suggesting specific neuronal functions in health and disease.
Keywords: CACNA2D; brain disease; cortical lamination; over-grooming; stereology; voltage-gated calcium channels.
Copyright © 2021 Geisler, Benedetti, Schöpf, Schwarzer, Stefanova, Schwartz and Obermair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Barclay J., Balaguero N., Mione M., Ackerman S. L., Letts V. A., Brodbeck J., et al. . (2001). Ducky mouse phenotype of epilepsy and ataxia is associated with mutations in the Cacna2d2 gene and decreased calcium channel current in cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Neurosci. 21, 6095–6104. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-06095.2001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

