Neuroprotective Role of GLP-1 Analog for Retinal Ganglion Cells via PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy in Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 33679385
- PMCID: PMC7928389
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.589114
Neuroprotective Role of GLP-1 Analog for Retinal Ganglion Cells via PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy in Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
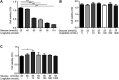
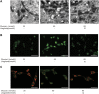
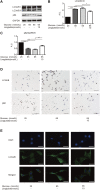
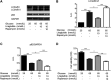
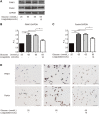
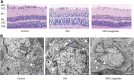
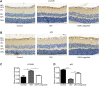
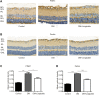
GLP-1 analogs have been widely used to treat patients with type 2 diabetes in recent years and studies have found that GLP-1 analogs have multiple organ benefits. However, the role of GLP-1 analogs in diabetic retinopathy (DR), a common complication of diabetes mellitus (DM), remains controversial. Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) are the only afferent neurons responsible for transmitting visual information to the visual center and are vulnerable in the early stage of DR. Protection of RGC is vital for visual function. The incretin glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which is secreted by L-cells after food ingestion, could lower blood glucose level through stimulating the release of insulin. In the present study, we evaluated the effects of GLP-1 analog on RGCs both in vitro and in vivo. We established diabetic rat models in vivo and applied an RGC-5 cell line in vitro. The results showed that in high glucose conditions, GLP-1 analog alleviated the damage of RGCs. In addition, GLP-1 analog prevented mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway. Here we demonstrated the neuroprotective effect of GLP-1 analog, which may be beneficial for retinal function, and we further elucidated a novel mechanism in GLP-1 analog-regulated protection of the retina. These findings may expand the multi-organ benefits of GLP-1 analogs and provide new insights for the prevention of DR.
Keywords: GLP-1; GLP-1 analog; diabetic retinopathy; mitophagy; retinal ganglion cell.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Ma, Lin, Hao, Yu, Li, Xu and Kuang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liraglutide alleviates H2O2-induced retinal ganglion cells injury by inhibiting autophagy through mitochondrial pathways.Peptides. 2017 Jun;92:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Peptides. 2017. PMID: 28450048
-
Topical ocular administration of the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide arrests hyperphosphorylated tau-triggered diabetic retinal neurodegeneration via activation of GLP-1R/Akt/GSK3β signaling.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Jul 15;153:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.04.018. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 31015047
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates damage to myopic RGCs probably through lncRNA-XR_002789763.1-mediated mitophagy.Chin Med. 2025 Feb 2;20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01058-5. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 39894836 Free PMC article.
-
The potential benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for diabetic retinopathy.Peptides. 2018 Feb;100:123-126. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Peptides. 2018. PMID: 28807775 Review.
-
Harnessing the therapeutic potential of glucagon-like peptide-1: a critical review.Treat Endocrinol. 2002;1(2):117-25. doi: 10.2165/00024677-200201020-00005. Treat Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 15765627 Review.
Cited by
-
Retinal Neurodegeneration in Diabetes: an Emerging Concept in Diabetic Retinopathy.Curr Diab Rep. 2021 Dec 13;21(12):65. doi: 10.1007/s11892-021-01428-x. Curr Diab Rep. 2021. PMID: 34902066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: a real-world data study from a global federated database.Diabetologia. 2024 Jul;67(7):1271-1282. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06132-5. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38584180 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-proteasome system in diabetic retinopathy.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 19;10:e13715. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13715. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35873915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of GLP-1 Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors on Diabetic Retinopathy Progression: An Aggregated Electronic Health Record Data Study.Am J Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep;265:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2024.04.010. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Am J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38636788
-
Unlocking the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in ocular therapeutics: from molecular pathways to clinical impact.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1618079. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1618079. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40777992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal R., Zhuang Y., Cummings B. P., Stanhope K. L., Graham J. L., Havel P. J., et al. (2014). Deterioration of plasticity and metabolic homeostasis in the brain of the UCD-T2DM rat model of naturally occurring type-2 diabetes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1842 (9), 1313–1323. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

