Pharmacological Therapies and Their Clinical Targets in Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Diarrhea
- PMID: 33679391
- PMCID: PMC7935509
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.629026
Pharmacological Therapies and Their Clinical Targets in Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Diarrhea
Abstract
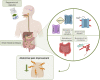
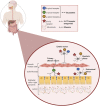
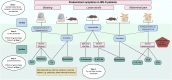
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the most common disorders of the gut-brain axis, which affects approximately 4% of the global population. The Rome IV criteria define IBS as chronic or recurrent abdominal pain associated with altered bowel habits. Patients can be categorized in four subtypes: IBS with predominant constipation (IBS-C), predominant diarrhea (IBS-D), mixed bowel habits (IBS-M), and unclassified (IBS-U). IBS is associated with a lower quality of life, reduced work productivity, and high healthcare costs. When comparing subtypes, patients with IBS-D report lower disease related quality of life. Due to the scope of this review, we have solely focused on patients with IBS-D. Choosing the right pharmacological treatment in these patients remains challenging due to the heterogeneous patient population, patients' expectation of the treatment outcome, unavailability of efficacious drugs, and the multifactorial and incompletely understood underlying pathophysiology. Currently, pharmacological treatment options target individual symptoms, such as abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, and bloating. In this review, we aimed to summarize the current and recent pharmacological treatment options in IBS-D, targeting the predominant gastrointestinal symptoms. Additionally, we proposed a pharmacological treatment algorithm which healthcare professionals could use when treating individual patients with IBS-D.
Keywords: abdominal pain; bloating; clinical management algorithms; diarrhea—therapy; irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea; loose stools; pharmacology.
Copyright © 2021 Colomier, Algera and Melchior.
Conflict of interest statement
CM has served as Consultant/Advisory Board member for Kyowa Kirin, Norgine, Biocodex, Mayoly spindler, Tillots and Ipsen. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome with mixed bowel habit pattern.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014 Jan;26(1):36-45. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12220. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014. PMID: 23991913 Free PMC article.
-
Updated review of current pharmacological and non-pharmacological management of irritable bowel syndrome.Life Sci. 2018 Nov 1;212:176-181. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30290187 Review.
-
Development of the Diary for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms to Assess Treatment Benefit in Clinical Trials: Foundational Qualitative Research.Value Health. 2017 Apr;20(4):618-626. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2016.11.001. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Value Health. 2017. PMID: 28408004
-
A diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome.Gastroenterology. 2014 Jan;146(1):67-75.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.09.046. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24076059 Clinical Trial.
-
Recent advances in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021 Aug 30;131(7-8):709-715. doi: 10.20452/pamw.16067. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34463082 Review.
Cited by
-
An Update on the Assessment and Management of Pediatric Abdominal Pain.Pediatric Health Med Ther. 2021 Aug 6;12:373-393. doi: 10.2147/PHMT.S287719. eCollection 2021. Pediatric Health Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34393542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Validation of a High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method to Quantify Marker Compounds in Lysimachia vulgaris var. davurica and Its Effects in Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Molecules. 2024 Mar 27;29(7):1489. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071489. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611770 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Overview of the Current Status and Advancements in Various Treatment Strategies against Epilepsy.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Nov 1;7(12):3729-3757. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00494. eCollection 2024 Dec 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39698272 Review.
-
Efficacy of acupuncture treatment for diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome with comorbid anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 15;103(46):e40207. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040207. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39560589 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Jawarish Shahi a herbal formulation in irritable bowel syndrome: An open-labeled single-arm clinical trial.J Tradit Complement Med. 2022 Apr 22;12(6):529-535. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.04.004. eCollection 2022 Nov. J Tradit Complement Med. 2022. PMID: 36325243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alammar N., Wang L., Saberi B., Nanavati J., Holtmann G., Shinohara R. T., et al. (2019). The impact of peppermint oil on the irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis of the pooled clinical data 11 medical and health sciences 1103 clinical sciences. BMC Compl. Alternative Med. 19, 21. 10.1186/s12906-018-2409-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

