Blood microRNA Signatures Serve as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Hepatic Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome Caused by Gynura japonica Containing Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids
- PMID: 33679405
- PMCID: PMC7933570
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.627126
Blood microRNA Signatures Serve as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Hepatic Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome Caused by Gynura japonica Containing Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids
Abstract
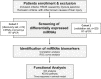
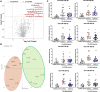
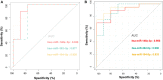
Background and Aims: The Gynura japonica-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (HSOS) is closely related to pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), and its prevalence has been increasing worldwide in recent years. However, no effective therapy for PA-induced HSOS in clinics is available, partially due to the failure of quick diagnosis. This study aims to identify blood microRNA (miRNA) signatures as potential biomarkers for PA-induced HSOS in clinics. Methods: The microarray-based miRNA profiling was performed on blood samples of the discovery cohort, which consisted of nine patients with HSOS and nine healthy donors. Differentially expressed miRNAs were further confirmed using a validation cohort, which consisted of 20 independent patients with HSOS. In addition, the rat model was established through the oral administration of the total alkaloid extract from G. japonica to investigate the association of miRNA biomarkers with the progression of HSOS. Bioinformatic analyses, including GO and KEGG enrichment, receiver operating characteristics curve, and correlation analyses were conducted to evaluate the accuracy of the potential miRNA biomarkers. Results: Three miRNAs, namely miR-148a-3p, miR-362-5p, and miR-194-5p, were overexpressed in patients and rats with PA-induced HSOS. These miRNAs were positively related to the severity of liver injury and displayed considerable diagnostic accuracy for patients with HSOS with areas under the curve over 0.87. Conclusion: In summary, this study demonstrated that three miRNAs, hsa-miR-148a-3p, hsa-miR-362-5p, and hsa-miR-194-5p, might serve as potential biomarkers for PA-induced HSOS in clinics.
Keywords: Gynura japonica; biomarker; diagnosis; hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome; microRNA; pyrrolizidine alkaloids.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Zhang, Yang, Chen, Zhuge, Xiong, Yang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tu-San-Qi (Gynura japonica): the culprit behind pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced liver injury in China.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Aug;42(8):1212-1222. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00553-9. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33154553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gynura Rhizoma containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids induces the hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in mice via upregulating fibrosis-related factors.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Jun;40(6):781-789. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0155-y. Epub 2018 Oct 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30367152 Free PMC article.
-
The long persistence of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-derived pyrrole-protein adducts in vivo: Kinetic study following multiple exposures of a pyrrolizidine alkaloid containing extract of Gynura japonica.Toxicol Lett. 2020 May 1;323:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.01.021. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31982501
-
Functional metabolomics characterizes the contribution of farnesoid X receptor in pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Aug;98(8):2557-2576. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03762-x. Epub 2024 May 4. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38703205
-
Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome associated with consumption of Gynura segetum.J Hepatol. 2011 Apr;54(4):666-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.031. Epub 2010 Sep 22. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21146894 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome: current advances and future perspectives.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Mar;99(3):835-850. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03950-9. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39718593 Review.
-
Identification of microRNAs Implicated in Modulating Senecionine-Induced Liver Toxicity in HepaRG Cells.Foods. 2022 Feb 12;11(4):532. doi: 10.3390/foods11040532. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35206009 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Toxification of 1,2-Unsaturated Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids Causes Human Hepatic Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome: The Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 27;22(19):10419. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910419. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

