Current Limitations and Candidate Potential of 5-HT7 Receptor Antagonism in Psychiatric Pharmacotherapy
- PMID: 33679481
- PMCID: PMC7930824
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.623684
Current Limitations and Candidate Potential of 5-HT7 Receptor Antagonism in Psychiatric Pharmacotherapy
Abstract
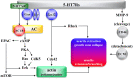
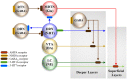
Several mood-stabilizing atypical antipsychotics and antidepressants weakly block serotonin (5-HT) receptor type-7 (5-HT7R); however, the contributions of 5-HT7R antagonism to clinical efficacy and pathophysiology are yet to be clarified. A novel mood-stabilizing antipsychotic agent, lurasidone exhibits predominant binding affinity to 5-HT7R when compared with other monoamine receptors. To date, we have failed to discover the superior clinical efficacy of lurasidone on schizophrenia, mood, or anxiety disorders when compared with conventional mood-stabilizing atypical antipsychotics; however, numerous preclinical findings have indicated the possible potential of 5-HT7R antagonism against several neuropsychiatric disorders, as well as the generation of novel therapeutic options that could not be expected with conventional atypical antipsychotics. Traditional experimental techniques, electrophysiology, and microdialysis have demonstrated that the effects of 5-HT receptor type-1A (5-HT1AR) and 5-HT7R on neurotransmission are in contrast, but the effect of 5-HT1AR is more predominant than that of 5-HT7R, resulting in an insufficient understanding of the 5-HT7R function in the field of psychopharmacology. Accumulating knowledge regarding the pharmacodynamic profiles of 5-HT7R suggests that 5-HT7R is one of the key players in the establishment and remodeling of neural development and cytoarchitecture during the early developmental stage to the mature brain, and dysfunction or modulation of 5-HT7R is linked to the pathogenesis/pathophysiology of neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders. In this review, to explore candidate novel applications for the treatment of several neuropsychiatric disorders, including mood disorders, schizophrenia, and other cognitive disturbance disorders, we discuss perspectives of psychopharmacology regarding the effects of 5-HT7R antagonism on transmission and intracellular signaling systems, based on preclinical findings.
Keywords: 5-HT7; antipsychotics; bipolar disorder (BD); cognition; lurasidone; schizophrenia; transmission.
Copyright © 2021 Okubo, Hasegawa, Fukuyama, Shiroyama and Okada.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yamamura S, Hoshikawa M, Dai K, Saito H, Suzuki N, Niwa O, et al. ONO-2506 inhibits spike-wave discharges in a genetic animal model without affecting traditional convulsive tests via gliotransmission regulation. Br J Pharmacol. (2013) 168:1088–100. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02132.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

