Inhibition of Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor Suppresses Neuroinflammation and Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
- PMID: 33679579
- PMCID: PMC7930561
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.607370
Inhibition of Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor Suppresses Neuroinflammation and Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
Abstract
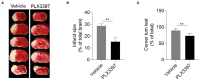
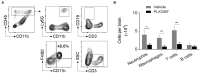
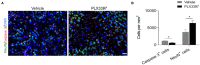
Hypoxic-ischemic (HI) brain injury is a major cause of neonatal death or lifetime disability without widely accepted effective pharmacological treatments. It has been shown that the survival of microglia requires colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) signaling and microglia participate in neonatal HI brain injury. We therefore hypothesize that microglia depletion during a HI insult period could reduce immature brain injury. In this study, CD1 mouse pups were treated with a CSF1R inhibitor (PLX3397, 25 mg/kg/daily) or a vehicle from postnatal day 4 to day 11 (P4-11), and over 90% of total brain microglia were deleted at P9. Unilateral hemisphere HI injury was induced at P9 by permanently ligating the left common carotid arteries and exposing the pups to 10% oxygen for 30 min to produce moderate left hemisphere injury. We found that the PLX3397 treatment reduced HI brain injury by 46.4%, as evaluated by the percentage of brain infarction at 48 h after HI. Furthermore, CSF1R inhibition suppressed the infiltration of neutrophils (69.7% reduction, p = 0.038), macrophages (77.4% reduction, p = 0.009), and T cells (72.9% reduction, p = 0.008) to the brain, the production of cytokines and chemokines (such as CCL12, CCL6, CCL21, CCL22, CCL19, IL7, CD14, and WISP-1), and reduced neuronal apoptosis as indicated by active caspase-3 labeled cells at 48 h after HI (615.20 ± 156.84/mm2 vs. 1,205.00 ± 99.15/mm2, p = 0.013). Our results suggest that CSF1R inhibition suppresses neuroinflammation and neonatal brain injury after acute cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal mice.
Keywords: PLX3397; colony stimulating factor 1 receptor; microglia; neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Ran, Wu, Zhang, Huang, Zhu, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rh-CSF1 attenuates neuroinflammation via the CSF1R/PLCG2/PKCε pathway in a rat model of neonatal HIE.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jun 10;17(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01862-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32522286 Free PMC article.
-
Atomoxetine, a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, improves short-term histological outcomes after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the neonatal male rat.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2018 Nov;70:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.03.011. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29608930
-
TNFR1-JNK signaling is the shared pathway of neuroinflammation and neurovascular damage after LPS-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic injury in the immature brain.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Dec 24;11:215. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0215-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 25540015 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen-rich saline promotes microglia M2 polarization and complement-mediated synapse loss to restore behavioral deficits following hypoxia-ischemic in neonatal mice via AMPK activation.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 May 18;16(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1488-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31103039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mediators of hypoxic-ischemic injury and implications for epilepsy in the developing brain.Epilepsy Behav. 2005 Sep;7(2):204-13. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2005.05.015. Epilepsy Behav. 2005. PMID: 16054439 Review.
Cited by
-
Microglial Depletion, a New Tool in Neuroinflammatory Disorders: Comparison of Pharmacological Inhibitors of the CSF-1R.Glia. 2025 Apr;73(4):686-700. doi: 10.1002/glia.24664. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Glia. 2025. PMID: 39719687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia and Stem-Cell Mediated Neuroprotection after Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Feb;18(2):474-522. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10213-y. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 34382141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia dynamic response and phenotype heterogeneity in neural regeneration following hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 29;14:1320271. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1320271. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38094292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced microglia activation following metformin administration or microglia ablation is sufficient to prevent functional deficits in a mouse model of neonatal stroke.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jun 15;19(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02487-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35705953 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of CSF1R, a receptor involved in microglia viability, alters behavioral and molecular changes induced by cocaine.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 6;11(1):15989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95059-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34362959 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

