Inhibition of Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor Suppresses Neuroinflammation and Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
- PMID: 33679579
- PMCID: PMC7930561
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.607370
Inhibition of Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor Suppresses Neuroinflammation and Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
Abstract
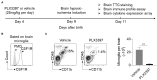
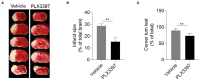
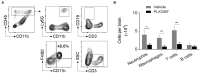
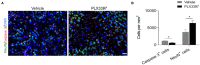
Hypoxic-ischemic (HI) brain injury is a major cause of neonatal death or lifetime disability without widely accepted effective pharmacological treatments. It has been shown that the survival of microglia requires colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) signaling and microglia participate in neonatal HI brain injury. We therefore hypothesize that microglia depletion during a HI insult period could reduce immature brain injury. In this study, CD1 mouse pups were treated with a CSF1R inhibitor (PLX3397, 25 mg/kg/daily) or a vehicle from postnatal day 4 to day 11 (P4-11), and over 90% of total brain microglia were deleted at P9. Unilateral hemisphere HI injury was induced at P9 by permanently ligating the left common carotid arteries and exposing the pups to 10% oxygen for 30 min to produce moderate left hemisphere injury. We found that the PLX3397 treatment reduced HI brain injury by 46.4%, as evaluated by the percentage of brain infarction at 48 h after HI. Furthermore, CSF1R inhibition suppressed the infiltration of neutrophils (69.7% reduction, p = 0.038), macrophages (77.4% reduction, p = 0.009), and T cells (72.9% reduction, p = 0.008) to the brain, the production of cytokines and chemokines (such as CCL12, CCL6, CCL21, CCL22, CCL19, IL7, CD14, and WISP-1), and reduced neuronal apoptosis as indicated by active caspase-3 labeled cells at 48 h after HI (615.20 ± 156.84/mm2 vs. 1,205.00 ± 99.15/mm2, p = 0.013). Our results suggest that CSF1R inhibition suppresses neuroinflammation and neonatal brain injury after acute cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal mice.
Keywords: PLX3397; colony stimulating factor 1 receptor; microglia; neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Ran, Wu, Zhang, Huang, Zhu, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

