Establishment and Application of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry for Detection of Shewanella Genus
- PMID: 33679644
- PMCID: PMC7930330
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.625821
Establishment and Application of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry for Detection of Shewanella Genus
Abstract
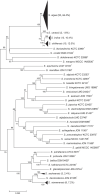
Shewanella species are widely distributed in the aquatic environment and aquatic organisms. They are opportunistic human pathogens with increasing clinical infections reported in recent years. However, there is a lack of a rapid and accurate method to identify Shewanella species. We evaluated here matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for rapid identification of Shewanella. A peptide mass reference spectra (PMRS) database was constructed for the type strains of 36 Shewanella species. The main spectrum projection (MSP) cluster dendrogram showed that the type strains of Shewanella species can be effectively distinguished according to the different MS fingerprinting. The PMRS database was validated using 125 Shewanella test strains isolated from various sources and periods; 92.8% (n = 116) of the strains were correctly identified at the species level, compared with the results of multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA), which was previously shown to be a method for identifying Shewanella at the species level. The misidentified strains (n = 9) by MALDI-TOF MS involved five species of two groups, i.e., Shewanella algae-Shewanella chilikensis-Shewanella indica and Shewanella seohaensis-Shewanella xiamenensis. We then identified and defined species-specific biomarker peaks of the 36 species using the type strains and validated these selected biomarkers using 125 test strains. Our study demonstrated that MALDI-TOF MS was a reliable and powerful tool for the rapid identification of Shewanella strains at the species level.
Keywords: MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry; Shewanella; detection; establishment and application; multilocus sequence analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Yu, Huang, Li, Fu, Lin, Wu, Dai, Cai, Xiao, Lan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
QF, LL, and SW were employed by the company Zybio Inc. Chongqing, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bao J. R., Master R. N., Azad K. N., Schwab D. A., Clark R. B., Jones R. S., et al. (2018). Rapid, accurate identification of candida auris by using a novel matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) database (Library). J. Clin. Microbiol. 56 e1700–e1717. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

