Microarray-Based Allergy Diagnosis: Quo Vadis?
- PMID: 33679689
- PMCID: PMC7928321
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.594978
Microarray-Based Allergy Diagnosis: Quo Vadis?
Abstract
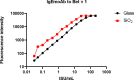
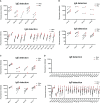
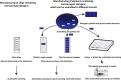
More than 30% of the world population suffers from allergy. Allergic individuals are characterized by the production of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies against innocuous environmental allergens. Upon allergen recognition IgE mediates allergen-specific immediate and late-phase allergic inflammation in different organs. The identification of the disease-causing allergens by demonstrating the presence of allergen-specific IgE is the key to precision medicine in allergy because it allows tailoring different forms of prevention and treatment according to the sensitization profiles of individual allergic patients. More than 30 years ago molecular cloning started to accelerate the identification of the disease-causing allergen molecules and enabled their production as recombinant molecules. Based on recombinant allergen molecules, molecular allergy diagnosis was introduced into clinical practice and allowed dissecting the molecular sensitization profiles of allergic patients. In 2002 it was demonstrated that microarray technology allows assembling large numbers of allergen molecules on chips for the rapid serological testing of IgE sensitizations with small volumes of serum. Since then microarrayed allergens have revolutionized research and diagnosis in allergy, but several unmet needs remain. Here we show that detection of IgE- and IgG-reactivity to a panel of respiratory allergens microarrayed onto silicon elements is more sensitive than glass-based chips. We discuss the advantages of silicon-based allergen microarrays and how this technology will allow addressing hitherto unmet needs in microarray-based allergy diagnosis. Importantly, it described how the assembly of silicon microarray elements may create different microarray formats for suiting different diagnostic applications such as quick testing of single patients, medium scale testing and fully automated large scale testing.
Keywords: IgE; allergen; allergen chip; allergy; microarrayed allergens; molecular diagnosis; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2021 Huang, Campana, Akinfenwa, Curin, Sarzsinszky, Karsonova, Riabova, Karaulov, Niespodziana, Elisyutina, Fedenko, Litovkina, Smolnikov, Khaitov, Vrtala, Schlederer and Valenta.
Conflict of interest statement
RV has received research grants from HVD Life Science, Vienna, Austria, and Viravaxx, Vienna, Austria, and serves as a consultant for Viravaxx. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Advances in allergen-microarray technology for diagnosis and monitoring of allergy: the MeDALL allergen-chip.Methods. 2014 Mar 1;66(1):106-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.10.008. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Methods. 2014. PMID: 24161540 Free PMC article.
-
Microarrayed recombinant allergens for diagnosis of allergy.Clin Exp Allergy. 2003 Jan;33(1):7-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2003.01550.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003. PMID: 12534543 Review.
-
Microarrayed allergen molecules: diagnostic gatekeepers for allergy treatment.FASEB J. 2002 Mar;16(3):414-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0711fje. Epub 2002 Jan 14. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 11790727
-
Microarrayed allergens for IgE profiling.Methods. 2004 Mar;32(3):249-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2003.08.018. Methods. 2004. PMID: 14962759 Review.
-
Maternal allergen-specific IgG might protect the child against allergic sensitization.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Aug;144(2):536-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.11.051. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30685457 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Allergen Microarrays and New Physical Approaches to More Sensitive and Specific Detection of Allergen-Specific Antibodies.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 20;14(7):353. doi: 10.3390/bios14070353. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cumulative IgE-levels specific for respiratory allergens as biomarker to predict efficacy of anti-IgE-based treatment of severe asthma.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 21;13:941492. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.941492. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36211434 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent IgE recognition of Blomia tropicalis allergen molecules in asthmatic children and young adults in equatorial Africa.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 2;14:1133935. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1133935. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37359512 Free PMC article.
-
Specific IgE and Basophil Activation Test by Microarray: A Promising Tool for Diagnosis of Platinum Compound Hypersensitivity Reactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 31;25(7):3890. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073890. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612700 Free PMC article.
-
Component-Resolved and Multiplex-Specific IgE Diagnostics: Utility in Anaphylaxis and Beyond.Children (Basel). 2025 Jul 16;12(7):933. doi: 10.3390/children12070933. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hofmaier S, Hatzler L, Rohrbach A, Panetta V, Hakimeh D, Bauer CP, et al. . “Default” versus “pre-atopic” IgG responses to foodborne and airborne pathogenesis-related group 10 protein molecules in birch-sensitized and nonatopic children. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2015) 135(5):1367–74.e1-8. 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.09.048 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

