The Immune System Can Hear Noise
- PMID: 33679706
- PMCID: PMC7930229
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.619189
The Immune System Can Hear Noise
Abstract
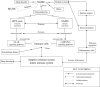
As a stressor widely existing in daily life, noise can cause great alterations to the immune system and result in many physical and mental disorders, including noise-induced deafness, sleep disorders, cardiovascular diseases, endocrine diseases and other problems. The immune system plays a major role in maintaining homeostasis by recognizing and removing harmful substances in the body. Many studies have shown that noise may play vital roles in the occurrence and development of some immune diseases. In humans, both innate immunity and specific immunity can be influenced by noise, and different exposure durations and intensities of noise may exert various effects on the immune system. Short-term or low-intensity noise can enhance immune function, while long-term or high-intensity noise suppresses it. Noise can lead to the occurrence of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) through the production of autoantibodies such as anti-Hsp70 and anti-Hsp60 and exert adverse effects related to other immune-related diseases such as some autoimmune diseases and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The neuroendocrine system, mainly including the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic-adrenal-medullary (SAM) system, is involved in the mechanisms of immune-related diseases induced by noise and gut microbiota dysfunction. In addition, noise exposure during pregnancy may be harmful to the immune system of the fetus. On the other hand, some studies have shown that music can improve immune function and alleviate the adverse effects caused by noise.
Keywords: immune diseases; immune function; music; noise; noise-induced hearing loss.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Zou, Guo, Wang, Shen, Hu, Ye and Xiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Frequency-specific association of antibodies against heat shock proteins 60 and 70 with noise-induced hearing loss in Chinese workers.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2004 Summer;9(2):207-13. doi: 10.1379/csc-12r.1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2004. PMID: 15497506 Free PMC article.
-
The sympathetic nerve--an integrative interface between two supersystems: the brain and the immune system.Pharmacol Rev. 2000 Dec;52(4):595-638. Pharmacol Rev. 2000. PMID: 11121511 Review.
-
Is there evidence that environmental noise is immunotoxic?Noise Health. 2009 Jul-Sep;11(44):151-5. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.53361. Noise Health. 2009. PMID: 19602768
-
Prenatal alcohol exposure and fetal programming: effects on neuroendocrine and immune function.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005 Jun;230(6):376-88. doi: 10.1177/15353702-0323006-05. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005. PMID: 15956767 Review.
-
[Immune outcomes of sleep disorders: the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as a modulatory factor].Braz J Psychiatry. 2007 May;29 Suppl 1:S33-8. doi: 10.1590/s1516-44462007000500007. Braz J Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17546346 Review. Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Environmental pollutants and phosphoinositide signaling in autoimmunity.J Hazard Mater. 2024 Mar 5;465:133080. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.133080. Epub 2023 Dec 1. J Hazard Mater. 2024. PMID: 38091799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Pueraria extracts on growth performance, immune function, and immune-related gene expression of Wuzhishan piglets.Front Vet Sci. 2025 May 30;12:1491130. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1491130. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520430 Free PMC article.
-
Health position paper and redox perspectives - Disease burden by transportation noise.Redox Biol. 2024 Feb;69:102995. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102995. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38142584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning-based urban noise appropriateness evaluation method and driving factor analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 23;19(12):e0311571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311571. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39715187 Free PMC article.
-
Home Environment as a Therapeutic Target for Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases: Delivering Restorative Living Spaces, Patient Education and Self-Care by Bridging Biophilic Design, E-Commerce and Digital Health Technologies.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Feb 5;22(2):225. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22020225. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40003451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Regional office for Europe . Burden of disease from environmental noise – Quantification of healthy life years lost in Europe. Copenhagen: (2011).
-
- Murphy E, King EA. Environmental Noise Pollution. Elsevier; (2014). pp. 51–80. 10.1016/B978-0-12-411595-8.00003-3 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

