Galaxy and MEAN Stack to Create a User-Friendly Workflow for the Rational Optimization of Cancer Chemotherapy
- PMID: 33679888
- PMCID: PMC7935533
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.624259
Galaxy and MEAN Stack to Create a User-Friendly Workflow for the Rational Optimization of Cancer Chemotherapy
Abstract
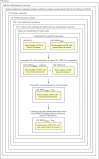
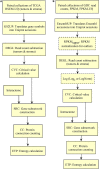
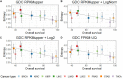
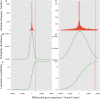
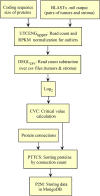
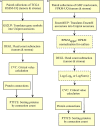
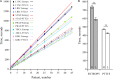
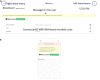
One aspect of personalized medicine is aiming at identifying specific targets for therapy considering the gene expression profile of each patient individually. The real-world implementation of this approach is better achieved by user-friendly bioinformatics systems for healthcare professionals. In this report, we present an online platform that endows users with an interface designed using MEAN stack supported by a Galaxy pipeline. This pipeline targets connection hubs in the subnetworks formed by the interactions between the proteins of genes that are up-regulated in tumors. This strategy has been proved to be suitable for the inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis in vitro. Therefore, Perl and Python scripts were enclosed in Galaxy for translating RNA-seq data into protein targets suitable for the chemotherapy of solid tumors. Consequently, we validated the process of target diagnosis by (i) reference to subnetwork entropy, (ii) the critical value of density probability of differential gene expression, and (iii) the inhibition of the most relevant targets according to TCGA and GDC data. Finally, the most relevant targets identified by the pipeline are stored in MongoDB and can be accessed through the aforementioned internet portal designed to be compatible with mobile or small devices through Angular libraries.
Keywords: Galaxy; MEAN stack; Shannon entropy; angular; personalized medicine; protein–protein network; systems biology; translational oncology.
Copyright © 2021 Pires, Silva, Weyssow, Conforte, Pagnoncelli, Silva and Carels.
Conflict of interest statement
The intellectual property of this research is protected by the Brazilian patent number BR1020150308191. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Strategy Utilizing Protein-Protein Interaction Hubs for the Treatment of Cancer Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 8;24(22):16098. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216098. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling Complexity Measured by Shannon Entropy and Its Application in Personalized Medicine.Front Genet. 2019 Oct 21;10:930. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00930. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31695721 Free PMC article.
-
MGEScan: a Galaxy-based system for identifying retrotransposons in genomes.Bioinformatics. 2016 Aug 15;32(16):2502-4. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw157. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27153595
-
ReGaTE: Registration of Galaxy Tools in Elixir.Gigascience. 2017 Jun 1;6(6):1-4. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/gix022. Gigascience. 2017. PMID: 28402416 Free PMC article.
-
RAP: RNA-Seq Analysis Pipeline, a new cloud-based NGS web application.BMC Genomics. 2015;16(Suppl 6):S3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S6-S3. Epub 2015 Jun 1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26046471 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessing RNA-Seq Workflow Methodologies Using Shannon Entropy.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;13(7):482. doi: 10.3390/biology13070482. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056677 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the pathogenesis of gastric intestinal metaplasia based on the mucosoid air-liquid interface.J Transl Med. 2024 May 17;22(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05276-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38760813 Free PMC article.
-
A Strategy Utilizing Protein-Protein Interaction Hubs for the Treatment of Cancer Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 8;24(22):16098. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216098. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Characterization of Heat Shock Protein 90β and Molecular Interactions with Geldanamycin and Ritonavir: A Computational Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 12;25(16):8782. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168782. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201468 Free PMC article.
-
A Data Science Approach for the Identification of Molecular Signatures of Aggressive Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 7;14(9):2325. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092325. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565454 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

