Reinforcement Learning in Neurocritical and Neurosurgical Care: Principles and Possible Applications
- PMID: 33680069
- PMCID: PMC7925047
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6657119
Reinforcement Learning in Neurocritical and Neurosurgical Care: Principles and Possible Applications
Abstract
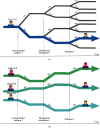
Dynamic decision-making was essential in the clinical care of surgical patients. Reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm is a computational method to find sequential optimal decisions among multiple suboptimal options. This review is aimed at introducing RL's basic concepts, including three basic components: the state, the action, and the reward. Most medical studies using reinforcement learning methods were trained on a fixed observational dataset. This paper also reviews the literature of existing practical applications using reinforcement learning methods, which can be further categorized as a statistical RL study and a computational RL study. The review proposes several potential aspects where reinforcement learning can be applied in neurocritical and neurosurgical care. These include sequential treatment strategies of intracranial tumors and traumatic brain injury and intraoperative endoscope motion control. Several limitations of reinforcement learning are representations of basic components, the positivity violation, and validation methods.
Copyright © 2021 Ying Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sutton R. S., Barto A. G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press; 2018.
-
- Stroup T. S., McEvoy J. P., Swartz M. S., et al. The National Institute of Mental Health Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) project: schizophrenia trial design and protocol development. Schizophrenia Bulletin. 2003;29(1):15–31. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a006986. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

