Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging: technique, guidelines and key applications
- PMID: 33680078
- PMCID: PMC7929776
- DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2021.1164
Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging: technique, guidelines and key applications
Abstract
Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) is an imaging method without ionising radiation that can provide WB coverage with a core protocol of essential imaging contrasts in less than 40 minutes, and it can be complemented with sequences to evaluate specific body regions as needed. In many cases, WB-MRI surpasses bone scintigraphy and computed tomography in detecting and characterising lesions, evaluating their response to therapy and in screening of high-risk patients. Consequently, international guidelines now recommend the use of WB-MRI in the management of patients with multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, melanoma and individuals with certain cancer predisposition syndromes. The use of WB-MRI is also growing for metastatic breast cancer, ovarian cancer and lymphoma as well as for cancer screening amongst the general population. In light of the increasing interest from clinicians and patients in WB-MRI as a radiation-free technique for guiding the management of cancer and for cancer screening, we review its technical basis, current international guidelines for its use and key applications.
Keywords: diffusion-weighted imaging; magnetic resonance imaging; oncology; whole-body.
© the authors; licensee ecancermedicalscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Summers is co-owner of QMRI Tech, a company that provides support for medical physics activities and MRI research. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
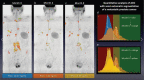


References
-
- Carriero A, Scarabino T, Magarelli N, et al. Whole-body magnetic resonance angiography using a contrast medium. Technical optimization. Radiol Med. 1997;94:319–324. - PubMed
-
- Westenberg JJ, Wasser MN, van der Geest RJ, et al. Scan optimization of gadolinium contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MRA of peripheral arteries with multiple bolus injections and in vitro validation of stenosis quantification. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;17:47–57. doi: 10.1016/S0730-725X(98)00152-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, et al. Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med. 2004;22:275–282. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
