Deep Learning-Driven Automated Detection of COVID-19 from Radiography Images: a Comparative Analysis
- PMID: 33680209
- PMCID: PMC7921610
- DOI: 10.1007/s12559-020-09779-5
Deep Learning-Driven Automated Detection of COVID-19 from Radiography Images: a Comparative Analysis
Abstract
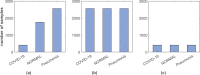
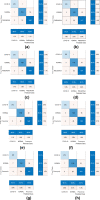
The COVID-19 pandemic has wreaked havoc on the whole world, taking over half a million lives and capsizing the world economy in unprecedented magnitudes. With the world scampering for a possible vaccine, early detection and containment are the only redress. Existing diagnostic technologies with high accuracy like RT-PCRs are expensive and sophisticated, requiring skilled individuals for specimen collection and screening, resulting in lower outreach. So, methods excluding direct human intervention are much sought after, and artificial intelligence-driven automated diagnosis, especially with radiography images, captured the researchers' interest. This survey marks a detailed inspection of the deep learning-based automated detection of COVID-19 works done to date, a comparison of the available datasets, methodical challenges like imbalanced datasets and others, along with probable solutions with different preprocessing methods, and scopes of future exploration in this arena. We also benchmarked the performance of 315 deep models in diagnosing COVID-19, normal, and pneumonia from X-ray images of a custom dataset created from four others. The dataset is publicly available at https://github.com/rgbnihal2/COVID-19-X-ray-Dataset. Our results show that DenseNet201 model with Quadratic SVM classifier performs the best (accuracy: 98.16%, sensitivity: 98.93%, specificity: 98.77%) and maintains high accuracies in other similar architectures as well. This proves that even though radiography images might not be conclusive for radiologists, but it is so for deep learning algorithms for detecting COVID-19. We hope this extensive review will provide a comprehensive guideline for researchers in this field.
Keywords: Automated detection; COVID-19; Deep learning; Medical imaging; Radiography; SARS-CoV-2.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Algorithm for COVID-19 Classification Using Chest X-Ray Images.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:9269173. doi: 10.1155/2021/9269173. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34795794 Free PMC article.
-
A Deep Learning Model for Diagnosing COVID-19 and Pneumonia through X-ray.Curr Med Imaging. 2023;19(4):333-346. doi: 10.2174/1573405618666220610093740. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 35692156
-
Deep-COVID: Predicting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning.Med Image Anal. 2020 Oct;65:101794. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101794. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Med Image Anal. 2020. PMID: 32781377 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of machine learning-based methods for COVID-19 medical image analysis.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023 Jun;61(6):1257-1297. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02758-y. Epub 2023 Jan 28. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023. PMID: 36707488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis: A comprehensive review of pre-trained deep learning models based on feature extraction algorithm.Results Eng. 2023 Jun;18:101020. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101020. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Results Eng. 2023. PMID: 36945336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-DSNet: A novel deep convolutional neural network for detection of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) cases from CT and Chest X-Ray images.Artif Intell Med. 2022 Dec;134:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102427. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Artif Intell Med. 2022. PMID: 36462906 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Implication and Prognostic Value of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Results of Chest Radiographs for Assessing Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 16;13(12):2090. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13122090. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370985 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Pandemic.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 26;13:845305. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.845305. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35559010 Free PMC article.
-
Learning effective embedding for automated COVID-19 prediction from chest X-ray images.Multimed Syst. 2023;29(2):739-751. doi: 10.1007/s00530-022-01015-4. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Multimed Syst. 2023. PMID: 36310764 Free PMC article.
-
COVIDXception-Net: A Bayesian Optimization-Based Deep Learning Approach to Diagnose COVID-19 from X-Ray Images.SN Comput Sci. 2022;3(2):115. doi: 10.1007/s42979-021-00980-3. Epub 2021 Dec 30. SN Comput Sci. 2022. PMID: 34981040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tavakoli M, Carriere J, Torabi A. 2020. Robotics, smart wearable technologies, and autonomous intelligent systems for healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic: an analysis of the state of the art and future vision. Advanced intelligent systems;n/a(n/a):2000071. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/aisy.202000071. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
