A universal model describing the structure and functions of living systems
- PMID: 33680281
- PMCID: PMC7906254
- DOI: 10.1080/19420889.2021.1887549
A universal model describing the structure and functions of living systems
Abstract
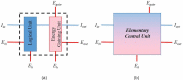
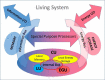
Can Life be explained based on the fundamental Laws of Nature? This question is central in Science since its answer could unify Physics and Biology and open new routes for Medicine. The present study introduces a clear and well-documented hypothesis addressing the unified description of all living systems. The proposed universal model is based on two established characteristics of Life. First, the concept of Functional Self-similarity (FSS) is introduced. As shown by several authors, all living systems can be classified in a multi-level hierarchy of increasing complexity. Systems in all hierarchical levels are characterized by a small set of the same attributes defining Life. This observation implies the existence of an elementary living system (i.e., a quantum of Life) having all the necessary functionalities of living systems. Secondly, the non-equilibrium nature of living systems implies that they should be able to process information since such a function is required for reducing entropy. Therefore, all living systems necessarily perform logical operations similar to electronic circuits. This conclusion, which is based on the requirement to overcome the constraints of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, indicates a close correspondence between living systems and information processing machines, namely computers. Consequently, important theoretical principles and concepts regarding computer design may also apply in the study of living systems. The above considerations lead to the Hypothesis of a Universal Architecture (UAH).
Keywords: Logic and Life; information and entropy; living systems; maxwell’s demon; self-similarity; thermodynamics.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author.
Figures
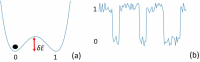
References
-
- Raven PH, Johnson GB, Mason KA, et al. Biology. 11th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2017. Chapter 1.
-
- Schrödinger E. What is life? Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1944.
-
- Prigogine I. From being to becoming. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company; 1980.
-
- Shannon CE. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J. 1948;27(3):379–423.
-
- Brillouin L. The negentropy principle of information. J. of Applied Physics. 1953;24(9):1152–1163.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
