COVID-19 pandemic: Can zinc supplementation provide an additional shield against the infection?
- PMID: 33680350
- PMCID: PMC7923946
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.02.015
COVID-19 pandemic: Can zinc supplementation provide an additional shield against the infection?
Abstract
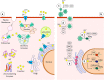
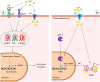
Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19)-induced severe acute respiratory syndrome is a global pandemic. As a preventive measure, human movement is restricted in most of the world. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), along with the World Health Organization (WHO) have laid out some therapeutic guidelines for the infected patients. However, other than handwashing and vigilance surrounding commonly encountered oronasal symptoms and fever, no universally available prophylactic measure has yet been established. In a pandemic, the accessibility of a prophylactic biologically active substance is crucial. Ideally, it would be something readily available at a low price to a larger percentage of the population with minimal risk. Studies have demonstrated that zinc may reduce viral replication and increase immune responses. While consuming zinc (within the recommended upper safety limits), as a prophylactic might provide an additional shield against the initiation and progression of COVID-19 would need clinical studies, the potential clearly exists. Even after vaccination, low zinc status may affect the vaccination responses.
Keywords: Antiviral; COVID-19; Host resistance; Pandemic; Zinc.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 Pandemic: Can Maintaining Optimal Zinc Balance Enhance Host Resistance?Tohoku J Exp Med. 2020 Jul;251(3):175-181. doi: 10.1620/tjem.251.175. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32641644
-
Potential health benefits of zinc supplementation for the management of COVID-19 pandemic.J Food Biochem. 2021 Feb;45(2):e13604. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13604. Epub 2021 Jan 17. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33458853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Reminder of Skin Cancer During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021 Apr;291(1):58. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021. PMID: 34477068
-
Handwashing in averting infectious diseases: Relevance to COVID-19.J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 12;27(S Pt 1):e37-e52. doi: 10.15586/jptcp.v27SP1.711. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32757544 Review.
-
A Case-Control Study for the Effectiveness of Oral Zinc in the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 13;8:756707. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.756707. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34966750 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A six-month study of anti-SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination: A comparative analysis of essential trace elements and anti-RBD IgG sera levels.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022 Dec;74:127079. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127079. Epub 2022 Sep 15. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36152463 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: Reducing the risk via diet and lifestyle.J Integr Med. 2023 Jan;21(1):1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2022.10.001. Epub 2022 Oct 10. J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36333177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Micronutrients and Toxic Metals in the Management of Epidemics in Cambodia.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 30;18(21):11446. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111446. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34769963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum zinc and copper in people with COVID-19 and zinc supplementation in parenteral nutrition.Nutrition. 2021 Nov-Dec;91-92:111467. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111467. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Nutrition. 2021. PMID: 34592694 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroquine chaos and COVID-19: Smart delivery perspectives through pH sensitive polymers/micelles and ZnO nanoparticles.Arab J Chem. 2023 Feb;16(2):104468. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104468. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Arab J Chem. 2023. PMID: 36466721 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gaur S., Agnihotri R. Trace mineral micronutrients and chronic periodontitis-a review. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017;176:225–238. - PubMed
-
- Kambe T., Tsuji T., Hashimoto A., Itsumura N. The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2015;95:749–784. - PubMed
-
- Kaur K., Gupta R., Saraf S.A., Saraf S.K. Zinc: the metal of life. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2014;13:358–376. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
