Different responses of normal cells (red blood cells) and cancer cells (K562 and K562/Dox cells) to low-dose 137Cs gamma-rays
- PMID: 33680462
- PMCID: PMC7922799
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2021.2236
Different responses of normal cells (red blood cells) and cancer cells (K562 and K562/Dox cells) to low-dose 137Cs gamma-rays
Abstract
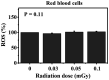
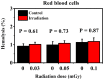
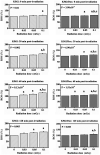
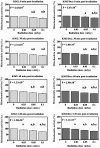
High-dose radiation is deleterious to cells or tissues. However, the health risks of exposure to low-dose radiation remain unclear. The present study aimed to investigate the biological responses of low-dose gamma-ray in vitro exposure to normal red blood cells (RBCs) and erythroleukemia (K562 and K562/Dox) cancer cells. Cells were given a low dose of 0.03, 0.05 and 0.1 mGy of 137Cs gamma-rays (at a dose rate of 0.001 Gy/min) under in vitro conditions. Cells exposed to 0 Gy served as controls. Hemolysis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured in exposed RBCs following exposure to low-dose gamma-rays. In addition, complete blood count (CBC) parameters were determined in irradiated whole blood. For irradiated K562 and K562/Dox cancer cells, ROS and mitochondrial activity were measured at 0, 30, 60 and 120 post-irradiation times. The results showed no change in the percentage of ROS and hemolysis in irradiated RBCs. The data indicated no perturbation in the CBC parameters in irradiated whole blood. By contrast, statistically significant dose-dependent increases in the percentage of ROS and decreases in the mitochondrial activity in the K562 and K562/Dox cancer cells were observed from 0 min up to 120 min post-irradiation. These findings concluded that there were differences in biological responses in normal cells (RBCs) and cancer cells (K562 and K562/Dox) to low-dose gamma-rays when cells were irradiated under in vitro conditions.
Keywords: blood; cancer; gamma-ray; low-dose radiation; radiation.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of pre-low-dose irradiation on anticancer activities of gallic acid in leukemic K562 and K562/Dox cells: cell viability and cellular energetic state studies.Med Oncol. 2022 Sep 29;39(12):229. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01835-4. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36175689
-
Effects of low-dose radiation on human blood components after in vitro exposure to gamma radiation from 137Cs radioactivity.Appl Radiat Isot. 2023 Feb;192:110577. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110577. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Appl Radiat Isot. 2023. PMID: 36459900
-
Susceptibility of oxidative stress on red blood cells exposed to gamma rays: hemorheological evaluation.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2008;40(4):315-24. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2008. PMID: 19126995
-
[Induction of glutathione and activation of immune functions by low-dose, whole-body irradiation with gamma-rays].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006 Oct;126(10):849-57. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.126.849. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 17016016 Review. Japanese.
-
Genotoxic and reprotoxic effects of tritium and external gamma irradiation on aquatic animals.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2012;220:67-103. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-3414-6_3. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22610297 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of pre-low-dose irradiation on anticancer activities of gallic acid in leukemic K562 and K562/Dox cells: cell viability and cellular energetic state studies.Med Oncol. 2022 Sep 29;39(12):229. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01835-4. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36175689
References
-
- Jelveh S, Kaspler P, Bhogal N, Mahmood J, Lindsay PE, Okunieff P, Doctrow SR, Bristow RG, Hill RP. Investigations of antioxidant-mediated protection and mitigation of radiation-induced DNA damage and lipid peroxidation in murine skin. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013;89:618–627. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2013.782450. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
