Exosome-mediated communication between tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages: implications for tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 33680573
- PMCID: PMC7901554
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1887552
Exosome-mediated communication between tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages: implications for tumor microenvironment
Abstract
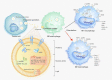
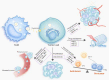
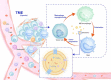
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles released from numerous types of cells that are involved in multiple tumors development. Exosomes contribute to the modulation of tumor microenvironment (TME) through intercellular communication. As essential immune stromal cells in the TME, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) participate in tumor development by mediating angiogenesis, metastasis, chemoresistance, and immune escape. Due to communication with multiple cells in the TME, they exhibit plasticity and heterogeneity during the progress of polarization from monocytes to macrophages. Previous studies suggest that targeting TAMs is a promising therapeutic strategy; however, the detailed mechanism by which TAMs regulate tumor development still remains unclear. In this review, we provide an overview of the roles of exosomes as messengers in the communication between tumor cells and polarization of TAMs; we also describe the effects of their interaction on tumor development. Finally, we comprehensively discussed the potential application of exosomes as the promising tumor immunotherapy strategy.
Keywords: Exosomes; cellular communication; polarization; tumor-associated macrophages.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomes: A Potential Therapeutic Tool Targeting Communications between Tumor Cells and Macrophages.Mol Ther. 2020 Sep 2;28(9):1953-1964. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.06.003. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32563274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-mediated communication between gastric cancer cells and macrophages: implications for tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 22;15:1327281. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1327281. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38455041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal ncRNAs facilitate interactive 'dialogue' between tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages.Cancer Lett. 2023 Jan 1;552:215975. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215975. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36306940 Review.
-
Crosstalk between exosomes and tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma: implication for cancer progression and therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1512480. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1512480. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40264760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Manipulated Small Extracellular Vesicles to Subvert Immunosuppression at the Tumor Microenvironment through Mannose Receptor/CD206 Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6318. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176318. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32878276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer derived exosomes induce macrophages immunosuppressive polarization to promote bladder cancer progression.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Sep 14;19(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00768-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34521440 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in major human diseases.EMBO J. 2021 Oct 1;40(19):e108863. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108863. Epub 2021 Aug 30. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34459017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-associated exosomes in cancer progression and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 7;5(9):e709. doi: 10.1002/mco2.709. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39247621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-derived exosomal linc00881 induces lung fibroblast activation and promotes osteosarcoma lung migration.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 21;23(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03121-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37990331 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal cargos-mediated metabolic reprogramming in tumor microenvironment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 10;42(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02634-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36899389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials