Characterization of Inflammatory and Fibrotic Aspects of Tissue Remodeling of Acellular Dermal Matrix in a Nonhuman Primate Model
- PMID: 33680668
- PMCID: PMC7928538
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003420
Characterization of Inflammatory and Fibrotic Aspects of Tissue Remodeling of Acellular Dermal Matrix in a Nonhuman Primate Model
Abstract
Human acellular dermal matrices (hADMs) are applied in various soft tissue reconstructive surgeries as scaffolds to support tissue remodeling and regeneration. To evaluate the clinical efficacy of hADM implants, it is integral that the hADM does not induce a host chronic inflammatory response leading to fibrotic encapsulation of the implant. In this study, we characterized the inflammatory and fibrosis-related tissue remodeling response of 2 commercial hADM products (SimpliDerm and AlloDerm RTU) in a nonhuman primate model using histology and gene expression profiling.
Methods: Eighteen African green monkeys with abdominal wall defects were applied to evaluate the performance of SimpliDerm and AlloDerm RTU implants (N = 3) at 2, 4, and 12-weeks post-implantation. Using histology and gene expression profiling, tissue responses such as implant integration, degradation, cell infiltration, immune response, neovascularization, and pro-fibrotic responses over time were evaluated.
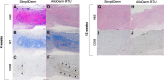
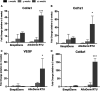
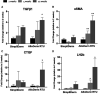
Results: SimpliDerm showed a lower initial inflammatory response and slower implant degradation rate than AlloDerm RTU evidenced by histomorphological analysis. These factors led to a more anti-inflammatory and pro-remodeling microenvironment within SimpliDerm, demonstrated by lower TNFα levels and lower expression levels of pro-fibrotic markers, and promoted tissue repair and regeneration by 3-months post-implantation.
Conclusions: Overall, histology and gene expression profiling analyses shown in this study demonstrated an effective model for analyzing hADM performance in terms of host inflammatory and fibrotic response. Further studies are warranted to fully evaluate the utility of this novel hADM in the clinical setting and verify the prognosis of our pre-clinical analysis model.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of 30-day Clinical Outcomes with SimpliDerm and AlloDerm RTU in Immediate Breast Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Jun 16;9(6):e3648. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003648. eCollection 2021 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 34150429 Free PMC article.
-
Vascularization of Human Acellular Dermal Matrices: A Comparative Study in a Nonhuman Primate Model.Tissue Eng Part A. 2025 May;31(9-10):419-432. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2024.0059. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Tissue Eng Part A. 2025. PMID: 39041614
-
Clinical Outcomes of Acellular Dermal Matrix (SimpliDerm and AlloDerm Ready-to-Use) in Immediate Breast Reconstruction.Cureus. 2022 Feb 18;14(2):e22371. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22371. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35198340 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical applications of acellular dermal matrices: A review.Scars Burn Heal. 2022 Jan 19;8:20595131211038313. doi: 10.1177/20595131211038313. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Scars Burn Heal. 2022. PMID: 35083065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cost effectiveness of acellular dermal matrix in expander-implant immediate breast reconstruction.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014 Apr;67(4):468-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.12.035. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014. PMID: 24508194 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Allogeneic Human Acellular Dermal Matrix Reduces the Incidence of Fistula in Hypospadias Repair.Front Pediatr. 2022 Mar 9;10:774973. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.774973. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35356442 Free PMC article.
-
Red Breast Syndrome and Acellular Dermal Matrix.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023 Jun 12;11(6):e5062. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005062. eCollection 2023 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023. PMID: 37313484 Free PMC article.
-
In-Vivo Evaluation of a Reinforced Ovine Biologic for Plastic and Reconstructive Procedures in a Non-human Primate Model of Soft Tissue Repair.Eplasty. 2022 Sep 14;22:e43. eCollection 2022. Eplasty. 2022. PMID: 36160663 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 30-day Clinical Outcomes with SimpliDerm and AlloDerm RTU in Immediate Breast Reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Jun 16;9(6):e3648. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003648. eCollection 2021 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 34150429 Free PMC article.
-
Acellular dermal matrix in reconstructive surgery: Applications, benefits, and cost.Front Transplant. 2023 Mar 10;2:1133806. doi: 10.3389/frtra.2023.1133806. eCollection 2023. Front Transplant. 2023. PMID: 38993878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brewer MB, Rada EM, Milburn ML, et al. . Human acellular dermal matrix for ventral hernia repair reduces morbidity in transplant patients. Hernia. 2011; 15:141–145. - PubMed
-
- Venturi ML, Mesbahi AN, Boehmler JH, IV, et al. . Evaluating sterile human acellular dermal matrix in immediate expander-based breast reconstruction: a multicenter, prospective, cohort study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 131:9e–18e - PubMed
-
- Banyard DA, Bourgeois JM, Widgerow AD, et al. . Regenerative biomaterials: a review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015; 135:1740–1748 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
