Comparative outcome analysis of spinal anesthesia versus general anesthesia in lumbar fusion surgery
- PMID: 33680810
- PMCID: PMC7919949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.11.017
Comparative outcome analysis of spinal anesthesia versus general anesthesia in lumbar fusion surgery
Abstract
Introduction: Spinal anesthesia (SA) has been shown in several studies to be a viable alternative to general anesthesia (GA) in laminectomies, discectomies, and microdiscectomies. However, the use of SA in spinal fusion surgery has been very scarcely documented in the current literature. Here we present a comparison of SA to GA in lumbar fusion surgery in terms of perioperative outcomes and cost.
Methods: The authors retrospectively reviewed the charts of all patients who underwent 1- or 2-level minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) surgery by a single surgeon, at a single institution, from 2015 to 2018. Data collected included demographics, operative and recovery times, nausea/vomiting, postoperative pain, and opioid requirement. Costs were included in the analysis if they were: 1) non-fixed; 2) incurred in the operating room (OR); and 3) directly related to patient care. All cost data represents net costs and was obtained from the hospital revenue cycle team. Patients were grouped for statistical analysis based on anesthetic modality.
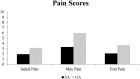
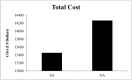
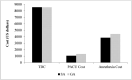
Results: A total of 29 patients received SA and 46 received GA. Both groups were similar in terms of age, gender, BMI, number of levels operated upon, preoperative diagnosis, and medical comorbidities. The SA group spent less time in the OR (163.86 ± 9.02 vs. 195.63 ± 11.27 min, p < 0.05), PACU (82.00 ± 7.17 vs. 102.98 ± 8.46 min, p < 0.05), and under anesthesia (175.03 ± 9.31 vs. 204.98 ± 10.15 min, p < 0.05) than the GA group. Post-surgery OR time was significantly less with SA than with GA (6.00 ± 1.09 vs. 17.26 ± 3.05 min, p < 0.05); however, pre-surgery OR time was similar between groups (50.17 ± 3.08 vs. 56.17 ± 5.34 min, p = 0.061). The SA group also experienced less maximum postoperative pain (3.31 ± 1.41 out of 10 vs. 5.96 ± 0.84/10, p < 0.05) and required less opioid analgesics (2.38 ± 1.37 vs. 5.39 ± 0.84 doses, p < 0.05). Both groups experienced similar nausea or vomiting rates and adverse events postoperatively. Net operative cost was found to be $812.31 (5.6%) less with SA than with GA, although this difference was not significant (p = 0.225).
Discussion/conclusion: To our knowledge, SA is almost never used in lumbar fusion, and a cost-effectiveness comparison with GA has not been recorded. In this retrospective study, we demonstrate that the use of SA in lumbar fusion surgery leads to significantly shorter operative and recovery times, less postoperative pain and opioid usage, and slight cost savings over GA. Thus, we conclude that this anesthetic modality represents a safe and cost-effective alternative to GA in lumbar fusion.
Keywords: Comparative outcome analysis; General anesthesia; Lumbar fusion; Spinal anesthesia; Spine surgery.
© 2020 Delhi Orthopedic Association. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spinal versus general anesthesia for minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: implications on operating room time, pain, and ambulation.Neurosurg Focus. 2021 Dec;51(6):E3. doi: 10.3171/2021.9.FOCUS21265. Neurosurg Focus. 2021. PMID: 34852316
-
Spinal Anesthesia Results in Lower Costs Compared to General Anesthesia for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Fusion-A Matched Cohort Study.J Clin Med. 2025 May 30;14(11):3851. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113851. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507611 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal versus general anesthesia for lumbar spine surgery in high risk patients: Perioperative hemodynamic stability, complications and costs.J Clin Anesth. 2018 May;46:3-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Jan 6. J Clin Anesth. 2018. PMID: 29316474
-
Spinal anesthesia in awake surgical procedures of the lumbar spine: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 3709 patients.Neurosurg Focus. 2021 Dec;51(6):E7. doi: 10.3171/2021.9.FOCUS21464. Neurosurg Focus. 2021. PMID: 34852320
-
General Anaesthesia Versus Regional Anaesthesia For Lumbar Laminectomy: A Review Of The Modern Literature.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2020 Jul-Sep;32(3):400-404. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2020. PMID: 32829559 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of combined spinal-epidural versus general anesthesia with epidural catheter on postoperative quality of recovery after abdominal hysterectomy: a prospective observational study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Jul 31;25(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03252-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40745528 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Combined Anesthetic Technique to Improve the Surgical Working Conditions of Lumbar and Thoracolumbar Spine Surgery from a Spine Surgeon's Perspective: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study.Asian Spine J. 2023 Apr;17(2):285-292. doi: 10.31616/asj.2022.0198. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Asian Spine J. 2023. PMID: 36740951 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing relevance of minimally invasive spinal surgery.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021 Sep 23;22:101606. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.101606. eCollection 2021 Nov. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021. PMID: 34631413 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Thoracic spinal anesthesia with intrathecal sedation for lower back surgery: a retrospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 11;11:1387935. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1387935. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38665296 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative outcomes of awake spine surgery under spinal versus general anesthesia: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2024 Mar;33(3):985-1000. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-08071-y. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 38110776
References
-
- Jellish W.S., Thalji Z., Stevenson K. A prospective randomized study comparing short- and intermediate-term perioperative outcome variables after spinal or general anesthesia for lumbar disk and laminectomy surgery. Anesth Analg. 1996 Sep;83(3):559–564. - PubMed
-
- McLain R.F., Bell G.R., Kalfas I. Complications associated with lumbar laminectomy: a comparison of spinal versus general anesthesia. Spine. 2004 Nov 15;29(22):2542–2547. (Phila Pa 1976) - PubMed
-
- McLain R.F., Kalfas I., Bell G.R. Comparison of spinal and general anesthesia in lumbar laminectomy surgery: a case-controlled analysis of 400 patients. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005 Jan;2(1):17–22. - PubMed
-
- McLain R.F., Tetzlaff J.E., Bell G.R. Microdiscectomy: spinal anesthesia offers optimal results in general patient population. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2007;16(1):5–11. Spring. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
