Alcohol-associated liver disease: A review on its pathophysiology, diagnosis and drug therapy
- PMID: 33680863
- PMCID: PMC7910406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.02.010
Alcohol-associated liver disease: A review on its pathophysiology, diagnosis and drug therapy
Abstract
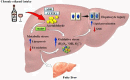
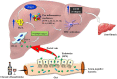
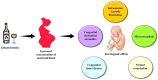
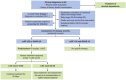
One of the global burdens of health care is an alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) and liver-related death which is caused due to acute or chronic consumption of alcohol. Chronic consumption of alcohol damage the normal defense mechanism of the liver and likely to disturb the gut barrier system, mucosal immune cells, which leads to decreased nutrient absorption. Therapy of ALD depends upon the spectrum of liver injury that causes fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. The foundation of therapy starts with abstinence from alcohol. Corticosteroids are used for the treatment of ALD but due to poor acceptance, continuing mortality, and identification of tumor necrosis factor-alpha as an integral component in pathogenesis, recent studies focus on pentoxifylline and, antitumor necrosis factor antibody to neutralize cytokines in the therapy of severe alcoholic hepatitis. Antioxidants also play a significant role in the treatment but till today there is no universally accepted therapy available for any stage of ALD. The treatment aspects need to restore the gut functions and require nutrient-based treatments to regulate the functions of the gut system and prevent liver injury. The vital action of saturated fatty acids greatly controls the gut barrier. Overall, this review mainly focuses on the mechanism of alcohol-induced metabolic dysfunction, contribution to liver pathogenesis, the effect of pregnancy, and targeted therapy of ALD.
Keywords: ALD, alcohol associated liver disease; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; Alcohol; CD14, cluster of differentiation14; CHD, congenital heart disease; ECM, extracellualr matrix; FASD, fetal alcohol spectrum disorders; FDA, food and drug administration; GGTP, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; GSH, Glutathione; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; HCV, chronic hepatitis C; HSC, hepatic stellate cells; IGR, intrauterine growth retardation; IL, interleukin; Immune modulation; JECH, Japan Environment and Children's Study; Liver pathogenesis; MDF, maddrey’s discriminant function; NA, nutritional assessment; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; NADPH, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; OLT, Orthotopic liver transplantation; Pregnancy; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TNF, Tumor necrosis factor; Targeted therapy.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

