Inhibition of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in Obese Male Mice Adversely Affects Reproductive Parameters
- PMID: 33680881
- PMCID: PMC7903665
- DOI: 10.18502/jri.v22i1.4991
Inhibition of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in Obese Male Mice Adversely Affects Reproductive Parameters
Abstract
Background: As obesity is increasing worldwide, obese people use various methods to get rid of excess weight. BMS309403 (A drug) is a specific inhibitor of fatty acid binding protein 4. In this study, the effects of the BMS309403 on serum biochemical markers, testis tissue spermatogenesis and apoptotic markers were investigated in male mice.
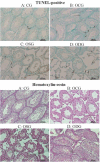
Methods: Balb/c mice (total=56, each group n=14) were divided into control, obese control, obese solvent and obese drug groups. The obese control, obese solvent and obese drug groups were fed on the high sucrose diet to lead to obesity. After the development of obesity, BMS309403 was orally administered to the obese drug group for six weeks. It was performed in testicular tissues (Johnson Score and apoptosis markers) and biochemical tests (total testosterone, sex hormone binding globulin, inhibin-B tests and free androgen index) were used to evaluate reproductive parameters. The p<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistical significance.
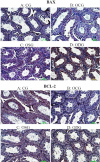
Results: Serum fatty acid binding protein 4 levels were higher in obese control group and obese solvent group, compared to control (p<0.05) and obese drug groups (p<0.001). Serum total testosterone, free androgen index, inhibin-B, sex hormone binding globulin levels, testicular tissue B-cell lymphoma-2 expression level and Johnson Score parameters were lower in all obese groups compared with the control group. Inhibin-B levels and Johnson Score results were lower in obese drug group compared to other two obese groups (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Contrary to expectations, the use of BMS309403 negatively affected male reproductive parameters. Negative changes in reproductive parameters may be a result of the increased lee index of obesity.
Keywords: BMS309403; Experimental obesity; Fatty acid binding protein 4; Male fertility impairment; Mice; Side-effects.
Copyright© 2021, Avicenna Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kralisch S, Fasshauer M. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein: a novel adipokine involved in the pathogenesis of metabolic and vascular disease? Diabetologia. 2013;56(1):10–21. - PubMed
-
- Okada T, Hiromura M, Otsuka M, Enomoto S, Miyachi H. Synthesis of BMS-309403-related compounds, including [14C]BMS-309403, a radioligand for adipocyte fatty acid binding protein. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2012;60(1):164–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
