ITM2A as a Tumor Suppressor and Its Correlation With PD-L1 in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 33680917
- PMCID: PMC7928367
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.581733
ITM2A as a Tumor Suppressor and Its Correlation With PD-L1 in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: High expression of integral membrane protein 2A (ITM2A) was reported to be associated with favorable prognosis in several solid tumors including breast cancer. This study aimed to investigate the role of ITM2A in breast cancer, especially in respect to tumor microenvironment.
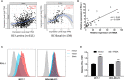
Methods: ITM2A expression was evaluated based on qRT-PCR results on breast cancer specimens, as well as TCGA and GEO datasets. The influence of ITM2A expression on breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth were evaluated by CCK-8 assay, clonogenic assay, and murine xenograft models. Transwell assay was performed to observe the changes of invasion and migration capacity in breast cancer cells. To determine the biological functions of ITM2A, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened based on RNA-sequencing data of MCF-7 cells overexpressed ITM2A. Then, functional annotation on DEGs was given by Gene Ontology and KEGG analysis. The stimulation on programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression when ITM2A overexpressed was determined by flow cytometry. Meanwhile, the correlation on expression levels between PD-L1 and ITM2A was tested via qRT-PCR on 24 breast cancer tissues, as well as public database.
Results: We demonstrated that ITM2A was frequently downregulated in breast cancer. Patients with high expression levels of ITM2A had longer overall survival and relapse free survival. Overexpression of ITM2A inhibited proliferation and impaired cells capacity of invasion and migration in vitro and in vivo. The DEGs in breast cancer cells overexpressed ITM2A were found to be associated with immunity responses. Moreover, ITM2A was found to facilitate breast cancer cells to express PD-L1. The correlation between PD-L1 and ITM2A was verified with both qRT-PCR assay and public database. Additionally, it was found that breast cancer had higher ITM2A expression frequently had more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs).
Conclusion: In summary, we found that high expression of ITM2A reduced the aggressivity of breast cancer cells and had a favorable effect on outcomes of patients with breast cancer. Moreover, ITM2A induced PD-L1 expression in breast cancer cells was accompanied with higher TILs numbers in tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: ITM2A; PD-L1; breast cancer; immune infiltration; prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Xu, Xia, Wang, Li and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integral membrane protein 2A inhibits cell growth in human breast cancer via enhancing autophagy induction.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Aug 22;17(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0422-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31438969 Free PMC article.
-
CMTM6 and PD-L1 coexpression is associated with an active immune microenvironment and a favorable prognosis in colorectal cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Feb;9(2):e001638. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001638. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33579737 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed Death Ligand 1 Indicates Pre-Existing Adaptive Immune Response by Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 17;20(20):5138. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205138. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31627272 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of evaluating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in breast cancer.Med Mol Morphol. 2017 Dec;50(4):185-194. doi: 10.1007/s00795-017-0170-y. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Med Mol Morphol. 2017. PMID: 28936553 Review.
-
Predictive Values of Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Expression for Prognosis, Clinicopathological Factors, and Response to Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Inhibitors in Patients With Gynecological Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 1;10:572203. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.572203. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33634012 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ITM2A inhibits the progression of bladder cancer by downregulating the phosphorylation of STAT3.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 May 15;14(5):2202-2215. doi: 10.62347/KHCC9690. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38859860 Free PMC article.
-
Integral membrane protein 2A enhances sensitivity to chemotherapy via notch signaling pathway in cervical cancer.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):10183-10193. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2001218. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34872446 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR1 Expression in MDA-PCa-2b Cell Upregulates ITM2A to Inhibit Tumor Growth.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 11;16(24):4138. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244138. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766038 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in PD-1-induced renal toxicity in patients with lung cancer.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Sep 14;25(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03754-0. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39277735 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive characterization of the molecular feature of T cells in laryngeal cancer: evidence from integrated single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data using multiple machine learning approaches.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2477287. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2477287. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40179028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Breast Cancer Facts & Figures. Am Cancer Soc (2021). Available at: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

