Pre- and Postoperative Models for Prediction of Recurrence in Non-B, Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 33680963
- PMCID: PMC7930483
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.612588
Pre- and Postoperative Models for Prediction of Recurrence in Non-B, Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background and aims: The incidence of non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma (NBNC-HCC) is increasing. Like in hepatitis B virus (HBC)/HCV-associated HCC, treatment of NBNC-HCC after resection is challenging due to its high recurrence rate. However, few studies on the recurrence of NBNC-HCC have been published in the past decades. Hence, we aimed to investigate the risk factors for recurrence of NBNC-HCC and construct pre- and postoperative prognostic models for predicting recurrence in these patients who underwent curative resection.
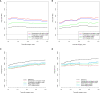
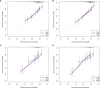
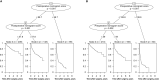
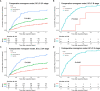
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 608 patients who underwent liver resection for NBNC-HCC. A multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was conducted to identify the independent risk factors of recurrence, based on which the prediction nomogram models were constructed and validated. The predictive performance of the models was assessed using the concordance index, time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curve, prediction error cure, and calibration curve. To facilitate clinical use, we stratified the patients into three distinct risk groups based on the score of the models. The cutoff scores of the models were determined by a survival tree analysis.
Results: Multivariable analysis identified neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, alpha fetoprotein, tumor number, and tumor diameter as independent preoperative risk factors for recurrence. In addition to these variables, microvascular invasion was an independent postoperative risk factor for recurrence. The pre- and postoperative nomograms were constructed based on these variables. The C-index of the pre- and postoperative nomograms was 0.689 and 0.702 in the training cohort, 0.682 and 0.688 in the validation cohort, respectively, which were both higher than those of the conventional Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) and 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC8th) staging systems. In addition, the pre- and postoperative nomograms could also re-stratify patients with BCLC stage 0/A or AJCC8th stage IA/IB/II into distinct risk groups.
Conclusions: We constructed pre- and postoperative prognostic models for predicting recurrence in patients with NBNC-HCC who underwent curative resection. They can play a supplementary role to the traditional staging system.
Keywords: inflammation; nomogram; non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma; recurrence; resection.
Copyright © 2021 Lin, Huang, Wang, Zeng, Ding, Liu, Fu, Guo, Chen, Zeng, Zhou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A nomogram predicting the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients after laparoscopic hepatectomy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019 Oct 11;39(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0404-6. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31601270 Free PMC article.
-
[The study of nomogram based on Ishak inflammation score for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Feb 1;56(2):124-129. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2018.02.009. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29397626 Chinese.
-
Development and validation of prognostic dynamic nomograms for hepatitis B Virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion after curative resection.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 19;13:1166327. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1166327. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37152055 Free PMC article.
-
Nomograms Incorporating the CNLC Staging System Predict the Outcome of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Curative Resection.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 21;11:755920. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.755920. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35127471 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Prognostic Nomogram to Predict the Long-Time Prognosis in Non-B, Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Aug 24;12:7771-7781. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S257016. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32943923 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic implications of alpha-fetoprotein and C-reactive protein elevation in hepatocellular carcinoma following resection (PACE): a large cohort study of 2770 patients.BMC Cancer. 2023 Dec 5;23(1):1190. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11693-6. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38053048 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative Adjuvant Transarterial Chemoembolization Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Multicentre Retrospective Study.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Mar 8;9:127-140. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S352480. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 35300207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Utsunomiya T, Shimada M, Kudo M, Ichida T, Matsui O, Izumi N, et al. . A comparison of the surgical outcomes among patients with HBV-positive, HCV-positive, and non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide study of 11,950 patients. Ann Surg (2015) 261(3):513–20. 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000821 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

