Molecular Subtype May Be More Associated With Prognosis and Chemotherapy Benefit Than Tumor Size in T1N0 Breast Cancer Patients: An Analysis of 2,168 Patients for Possible De-Escalation Treatment
- PMID: 33680973
- PMCID: PMC7933524
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.636266
Molecular Subtype May Be More Associated With Prognosis and Chemotherapy Benefit Than Tumor Size in T1N0 Breast Cancer Patients: An Analysis of 2,168 Patients for Possible De-Escalation Treatment
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer (BC) patients with T1N0 tumors have relatively favorable clinical outcomes. However, it remains unclear whether molecular subtypes can aide in prognostic prediction for such small, nodal-negative BC cases and guide decision-making about escalating or de-escalating treatments.
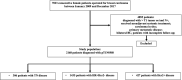
Patients and methods: T1N0 BC patients diagnosed between 2009 and 2017 were included and classified into three subgroups according to receptor status: 1) hormonal receptor (HR)+/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-; 2) HER2+; and 3) triple negative (TN) (HR-/HER2-). Patients' characteristics and relapse events were reviewed. Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression were used to assess the iDFS and BCSS. The effects of risk factors and adjuvant treatment benefits were evaluated by calculating hazard ratios (HRs) for invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) with Cox proportional hazards models.
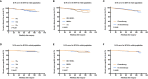
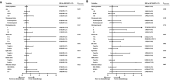
Results: In total, 2,168 patients (1,435 HR+/HER2-, 427 HER2+, 306 TN) were enrolled. The 5-year iDFS rates were 93.6, 92.7, and 90.6% for HR+/HER2-, HER2+, and TN patients, respectively (P = 0.039). Multivariate analysis demonstrated that molecular subtype (P = 0.043), but not tumor size (P = 0.805), was independently associated with iDFS in T1N0 BC. TN patients [HRs = 1.77, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.11-2.84, P = 0.018] had a higher recurrence risk than HR+/HER2- patients. Adjuvant chemotherapy benefit was not demonstrated in all T1N0 patients but interacted with molecular subtype status. TN (adjusted HRs = 2.31, 95% CI = 0.68-7.54) and HER2+ (adjusted HRs = 2.26, 95% CI = 0.95-5.63) patients receiving chemotherapy had superior iDFS rates. Regarding BCSS, molecular subtype tended to be related to outcome (P = 0.053) and associated with chemotherapy benefit (P = 0.005).
Conclusion: Molecular subtype was more associated with disease outcome and chemotherapy benefit than tumor size in T1N0 BC patients, indicating that it may guide possible clinical de-escalating therapy in T1N0 BC.
Keywords: breast cancer; chemotherapy benefit; de-escalating therapy; molecular subtype; prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhu, Li, Chen, Fei, Shen and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
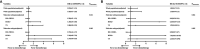
References
-
- Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A, III, et al. . AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer; (2010).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

