Adjunctive Immunotherapy With Polyclonal Ig-M Enriched Immunoglobulins for Septic Shock: From Bench to Bedside. The Rationale for a Personalized Treatment Protocol
- PMID: 33681248
- PMCID: PMC7930614
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.616511
Adjunctive Immunotherapy With Polyclonal Ig-M Enriched Immunoglobulins for Septic Shock: From Bench to Bedside. The Rationale for a Personalized Treatment Protocol
Abstract
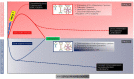
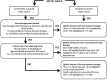
Septic shock still has a high mortality rate which has not hinted at decreasing in recent years. Unfortunately, randomized trials failed mainly because the septic patient was considered as a homogeneous entity. All this creates a sort of therapeutic impotence in everyday clinical practice in treating patients with septic shock. The need to customize therapy on each patient with sepsis has now become an established necessity. In this scenario, adjuvant therapies can help if interpreted as modulators of the immune system. Indeed, the host's immune response differs from patient to patient based on the virulence of the pathogen, comorbidity, infection site, and prolonged hospitalization. In this review, we summarize the rationale for using immunoglobulins as an adjunctive treatment. Furthermore, we would like to suggest a possible protocol to personalize treatment in the different clinical scenarios of the host's response to serious infectious events.
Keywords: adjunctive treatment; immunoglobulins; protocol; sepsis; septic shock.
Copyright © 2021 Busani, Roat, Tosi, Biagioni, Coloretti, Meschiari, Gelmini, Brugioni, De Biasi and Girardis.
Conflict of interest statement
MG has consulted for Biotest-Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham E, Anzueto A, Gutierrez G, Tessler S, San Pedro G, Wunderink R, et al. . Double-blind randomised controlled trial of monoclonal antibody to human tumour necrosis factor in treatment of septic shock. NORASEPT II study group. Lancet. (1998) 351:929–33. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)60602-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

