Capsule Size Alters the Timing of Metabolic Alkalosis Following Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation
- PMID: 33681279
- PMCID: PMC7933015
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.634465
Capsule Size Alters the Timing of Metabolic Alkalosis Following Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation
Abstract
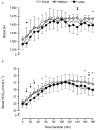
Introduction: Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is a well-established nutritional ergogenic aid that is typically ingested as a beverage or consumed in gelatine capsules. While capsules may delay the release of NaHCO3 and reduce gastrointestinal (GI) side effects compared with a beverage, it is currently unclear whether the capsule size may influence acid-base responses and GI symptoms following supplementation. Aim: This study aims to determine the effects of NaHCO3 supplementation, administered in capsules of different sizes, on acid-base responses, GI symptoms, and palatability. Methods: Ten healthy male subjects (mean ± SD: age 20 ± 2 years; height 1.80 ± 0.09 m; weight 78.0 ± 11.9 kg) underwent three testing sessions whereby 0.3 g NaHCO3/kg of body mass was consumed in either small (size 3), medium (size 0), or large (size 000) capsules. Capillary blood samples were procured pre-ingestion and every 10 min post-ingestion for 180 min. Blood samples were analyzed using a radiometer (Radiometer ABL800, Denmark) to determine blood bicarbonate concentration ([ ]) and potential hydrogen (pH). GI symptoms were measured using a questionnaire at the same timepoints, whereas palatability was recorded pre-consumption. Results: Capsule size had a significant effect on lag time (the time [ ] changed, T lag) and the timing of peak blood [ ] (T max). Bicarbonate T lag was significantly higher in the large-sized (28 ± 4 min) compared with the small-sized (13 ± 2 min) capsules (P = 0.009). Similarly, T max was significantly lower in the small capsule (94 ± 24 min) compared with both the medium-sized (141 ± 27 min; P < 0.001) and the large-sized (121 ± 29 min; P < 0.001) capsules. The GI symptom scores were similar for small-sized (3 ± 3 AU), medium-sized (5 ± 3 AU), and large-sized (3 ± 3 AU) capsules, with no significant difference between symptom scores (F = 1.3, P = 0.310). Similarly, capsule size had no effect on palatability (F = 0.8, P = 0.409), with similar scores between different capsule sizes. Conclusion: Small capsule sizes led to quicker T lag and T max of blood [ ] concentration compared to medium and large capsules, suggesting that individuals could supplement NaHCO3 in smaller capsules if they aim to increase extracellular buffering capacity more quickly.
Keywords: acid base balance; buffering; gastrointestinal disturbance; palatability; performance.
Copyright © 2021 Middlebrook, Peacock, Tinnion, Leach, Hilton, Saunders, Sparks and Mc Naughton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

