Metabolic Modeling to Interrogate Microbial Disease: A Tale for Experimentalists
- PMID: 33681294
- PMCID: PMC7930556
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.634479
Metabolic Modeling to Interrogate Microbial Disease: A Tale for Experimentalists
Abstract
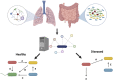
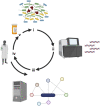
The explosion of microbiome analyses has helped identify individual microorganisms and microbial communities driving human health and disease, but how these communities function is still an open question. For example, the role for the incredibly complex metabolic interactions among microbial species cannot easily be resolved by current experimental approaches such as 16S rRNA gene sequencing, metagenomics and/or metabolomics. Resolving such metabolic interactions is particularly challenging in the context of polymicrobial communities where metabolite exchange has been reported to impact key bacterial traits such as virulence and antibiotic treatment efficacy. As novel approaches are needed to pinpoint microbial determinants responsible for impacting community function in the context of human health and to facilitate the development of novel anti-infective and antimicrobial drugs, here we review, from the viewpoint of experimentalists, the latest advances in metabolic modeling, a computational method capable of predicting metabolic capabilities and interactions from individual microorganisms to complex ecological systems. We use selected examples from the literature to illustrate how metabolic modeling has been utilized, in combination with experiments, to better understand microbial community function. Finally, we propose how such combined, cross-disciplinary efforts can be utilized to drive laboratory work and drug discovery moving forward.
Keywords: cystic fibrosis; drug discovery; gut microbiome; metabolic modeling; metabolite cross-feeding.
Copyright © 2021 Jean-Pierre, Henson and O’Toole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling approaches for probing cross-feeding interactions in the human gut microbiome.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Dec 8;20:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.12.006. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34976313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Modeling of Cystic Fibrosis Airway Communities Predicts Mechanisms of Pathogen Dominance.mSystems. 2019 Apr 23;4(2):e00026-19. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00026-19. eCollection 2019 Mar-Apr. mSystems. 2019. PMID: 31020043 Free PMC article.
-
Connect the dots: sketching out microbiome interactions through networking approaches.Microbiome Res Rep. 2023 Jul 18;2(4):25. doi: 10.20517/mrr.2023.25. eCollection 2023. Microbiome Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 38058764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One versus Many: Polymicrobial Communities and the Cystic Fibrosis Airway.mBio. 2021 Mar 16;12(2):e00006-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00006-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33727344 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological networking of cystic fibrosis lung infections.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2016 Dec 2;2:4. doi: 10.1038/s41522-016-0002-1. eCollection 2016. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2016. PMID: 28649398 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Symbiotic bacteria-mediated imbalance and repair of immune homeostasis: exploring novel mechanisms of microbiome-host interactions in atopic dermatitis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 23;16:1649857. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1649857. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40771817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How is the human microbiome linked to kidney stones?Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 6;15:1602413. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1602413. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40546285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota resilience and recovery after anticancer chemotherapy.Microbiome Res Rep. 2023 May 6;2(3):16. doi: 10.20517/mrr.2022.23. eCollection 2023. Microbiome Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 38046820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacomicrobiomics in Anticancer Therapies: Why the Gut Microbiota Should Be Pointed Out.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 24;14(1):55. doi: 10.3390/genes14010055. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36672796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial metabolism and pathogenesis intimate intertwining: time for metabolic modelling to come into action.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 Jan;15(1):95-102. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13942. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34672429 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

