Case Report: Hyperbilirubinemia in Gilbert Syndrome Attenuates Covid-19-Induced Metabolic Disturbances
- PMID: 33681310
- PMCID: PMC7925614
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.642181
Case Report: Hyperbilirubinemia in Gilbert Syndrome Attenuates Covid-19-Induced Metabolic Disturbances
Abstract
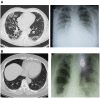
Gilbert syndrome (GS) is a liver disorder characterized by non-hemolytic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. On the other hand, Coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is a recent viral infectious disease presented as clusters of pneumonia, triggered by the severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Little is known on the association between SARS-CoV-2 and GS, despite different studies have recently stated a link between hyperbilirubinemia and SARS-CoV-2 severity. In this case-report study we described a 47-year-old man, a known case of GS since the age of 4, presented to the emergency department with fever (39.8°C), dry cough, dyspnea, headache, myalgia, sweating and jaundice diagnosed with Covid-19-induced pneumonia. Interestingly, GS patient exhibited a rapid clinical recovery and short hospital stay compared to other SARS-CoV-2 positive patient, seeming that hyperbilirubinemia may exert a protective effect of against Covid-19 induced-cardiometabolic disturbances. Data obtained here underlines that the higher resistance against Covid-19 evidenced by the GS patient seems to be due to the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects of unconjugated bilirubin.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; gilbert syndrome; hyperbilirubinemia; metabolic disease.
Copyright © 2021 Al-kuraishy, Al-Gareeb, Abdullah, Cruz-Martins and Batiha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary: Case Report: Hyperbilirubinemia in Gilbert Syndrome Attenuates Covid-19-Induced Metabolic Disturbances.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jul 22;8:685835. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.685835. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34368246 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous