Fracture of tibial tuberosity in an adult with Paget's disease of the bone - An interesting case and review of literature
- PMID: 33681443
- PMCID: PMC7930319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcr.2021.100440
Fracture of tibial tuberosity in an adult with Paget's disease of the bone - An interesting case and review of literature
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Patient Consent statement in previously published articles.Trauma Case Rep. 2023 Mar 1;45:100817. doi: 10.1016/j.tcr.2023.100817. eCollection 2023 Jun. Trauma Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37234574 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Paget's disease of the bone is a non-malignant skeletal disorder characterized by focal abnormalities in bone remodelling at one or more skeletal sites. Pathological fractures occurring from trivial injuries are a well-known clinical presentation in patients with Paget's disease. An avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity is an infrequent injury and has an extremely low occurrence in adults, with only a few cases reported in literature. We describe a case of a patient with undiagnosed Paget's Disease of the bone, sustaining a pathological avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity.
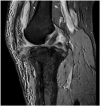
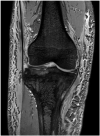
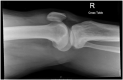
Case report: A 54-year-old male presented with right knee pain after his knee gave way whilst standing in the goal area during a game of football, twisting his right ankle and falling. Plain radiographs of the knee revealed an avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity with abnormal modelling of the proximal half of the tibia. An MRI confirmed a diagnosis of Paget's disease of the bone. The patient underwent open reduction internal fixation. At 3 months follow up, the patient had good knee range of motion from 0 to 100 degrees and by 6 months he had returned to his usual activities.
Conclusion: We describe a unique case of tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture in an adult with PDB. Treatment was successful with cannulated screws and tension band wiring. Patients with PDB who fracture present with diagnostic and operative challenges, it is vital to progress with caution in the postoperative rehabilitation phase.
Keywords: Adult fracture; Bone fragility; Paget's disease of the bone; Tibial tuberosity fracture.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- McKoy B.E., Stanitski C.L. Acute tibial tubercle avulsion fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2003;34:397–403. - PubMed
-
- Kang S., Chung P.H., Kim Y.S., Lee H.M., Kim J.P. Bifocal disruption of the knee extensor mechanism: a case report and literature review. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2013;133(4):517–521. - PubMed
-
- Jakoi A., Freidl M., Old A., Javandel M., Tom J., Realyvasquez J. Tibial tubercle avulsion fractures in adolescent basketball players. Orthopedics. 2012;35(8):692–696. - PubMed
-
- William L.H., Charles R.H., William D.A. Avulsion fractures of the tibial tubercle. J Bone Joint Surg Am The Journal Of Bone & Joint Surgery. 1971;53(8):1579–1583. - PubMed
-
- McKoy B.E., Stanitski C.L. Acute tibial tubercle avulsion fractures. The Orthopedic Clinics of North America. 2003;34(3):397–403. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

