Effect of 18-Crown-6 on Oxytocin Stability in Aqueous Buffer Solutions
- PMID: 33681619
- PMCID: PMC7931373
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06248
Effect of 18-Crown-6 on Oxytocin Stability in Aqueous Buffer Solutions
Abstract
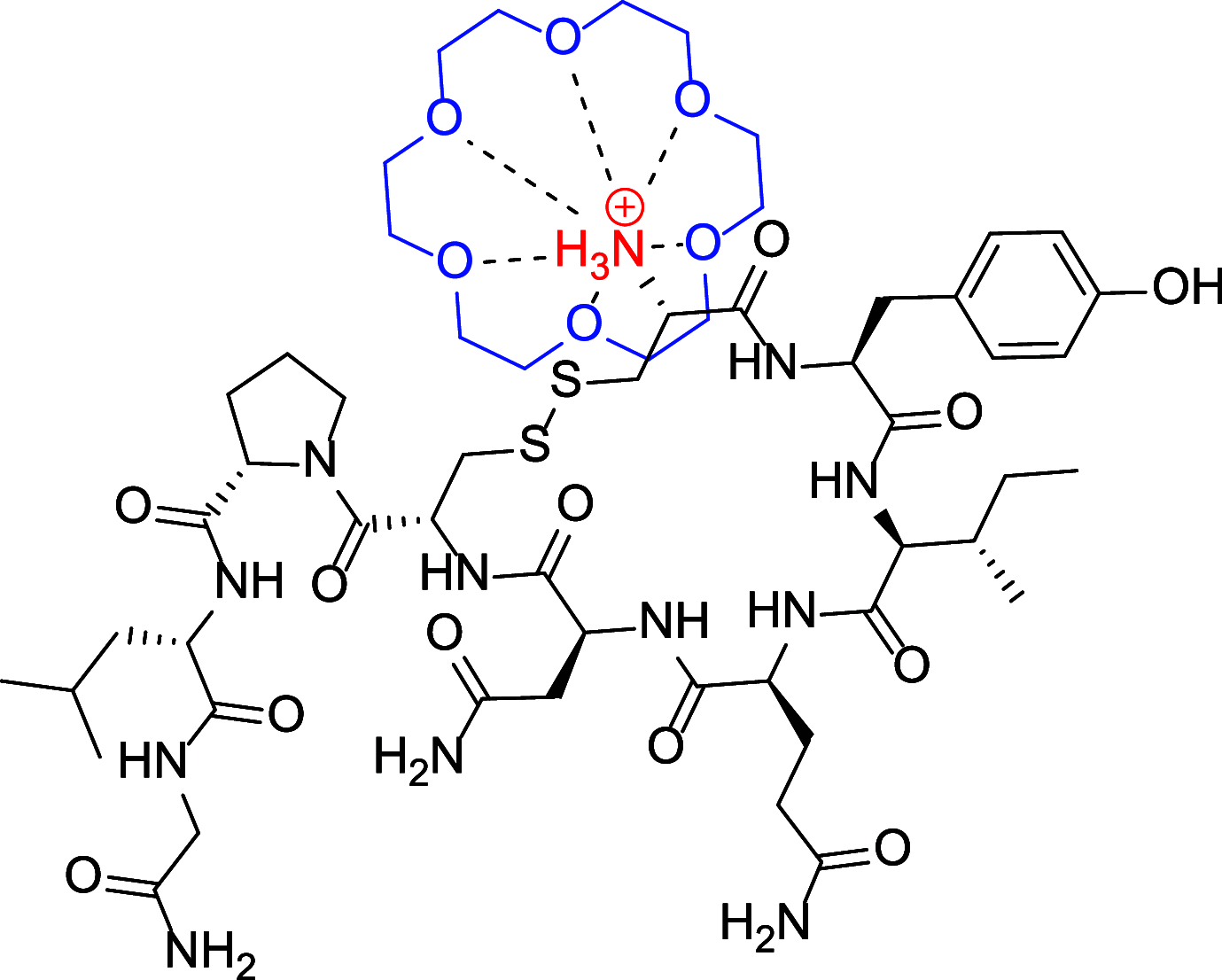
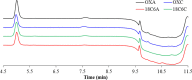
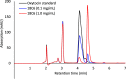
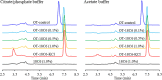
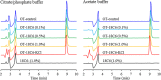
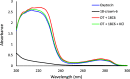
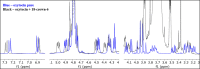
In this study, the effect of 18-crown-6 on the stability of oxytocin in aqueous solution was explored. The study found that while 12-crown-4 and 15-crown-5 do not stabilize oxytocin, 18-crown-6 does have a stabilizing effect in citrate/phosphate buffer at pH 4.5. However, in acetate buffer at the same pH, the presence of 18-crown-6 had a destabilizing effect, possibly leading to a different degradation pathway. Both the stabilizing and destabilizing effects, depending on the buffer used, are concentration dependent where a higher concentration of 18-crown-6 is linked to a stronger effect. It is hypothesized that this effect may be linked to 18-crown-6 binding to the protonated ammonium group of oxytocin. Upon changing the mobile phase used in high-performance liquid chromatography experiments, we observed evidence supporting this binding hypothesis. When an acidic mobile phase was used (0.01% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)), a partial shift in oxytocin retention time was observed for samples in acetate buffers in the presence of 18-crown-6 when using a 150 mm column (C18). The amount of the peak that shifted depended on the 18-crown-6 concentration used. A similar shift in oxytocin peak retention time was observed for samples in both acetate and citrate/phosphate buffers when using a 250 mm column (C18), but the peak completely shifted in those samples. When using an even more acidic mobile phase (0.1% TFA), the oxytocin peaks all had the same retention time again. Ultraviolet and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy experiments also showed that the presence of 18-crown-6 has an observable effect on the resulting oxytocin spectra.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new strategy to stabilize oxytocin in aqueous solutions: I. The effects of divalent metal ions and citrate buffer.AAPS J. 2011 Jun;13(2):284-90. doi: 10.1208/s12248-011-9268-7. Epub 2011 Mar 30. AAPS J. 2011. PMID: 21448747 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of mobile phase additives on solute retention at low aqueous pH in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 2017 Feb 3;1483:71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.035. Epub 2016 Dec 15. J Chromatogr A. 2017. PMID: 28069167
-
The effect of D-(+)-glucosamine, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and tetraethylene glycol on the stability of oxytocin in aqueous solution.Pharmazie. 2021 Oct 1;76(10):480-483. doi: 10.1691/ph.2021.1081. Pharmazie. 2021. PMID: 34620274
-
Study of retention and peak shape in hydrophilic interaction chromatography over a wide pH range.J Chromatogr A. 2015 Sep 11;1411:41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.092. Epub 2015 Jul 29. J Chromatogr A. 2015. PMID: 26275863
-
Determination of the pH of binary mobile phases for reversed-phase liquid chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 2004 May 28;1037(1-2):283-98. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2003.12.063. J Chromatogr A. 2004. PMID: 15214671 Review.
References
-
- Van Dongen P. W. J.; Van Roosmalen J.; De Boer C. N.; Van Rooij J. Oxytocics for the Prevention of Post-Partum Haemorrhages. Pharm. Weekbl. Sci. Ed 1991, 13, 238–243. - PubMed
-
- Olff M.; Frijling J. L.; Kubzansky L. D.; Bradley B.; Ellenbogen M. A.; Cardoso C.; Bartz J. A.; Yee J. R.; van Zuiden M. The Role of Oxytocin in Social Bonding, Stress Regulation and Mental Health: An Update on the Moderating Effects of Context and Interindividual Differences. Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2013, 38, 1883–1894. 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.06.019. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

